A Python Package for Computing Effective Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine Climate Data.

pyCropWat/
├── pycropwat/ # Main package
│ ├── __init__.py # Package exports
│ ├── core.py # EffectivePrecipitation class
│ ├── methods.py # Effective precipitation methods (9 methods)
│ ├── analysis.py # Temporal aggregation, statistics, visualization
│ ├── utils.py # Utility functions (geometry loading, GEE init)
│ └── cli.py # Command-line interface
├── tests/ # Unit tests
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── test_core.py
├── docs/ # MkDocs documentation
│ ├── index.md # Documentation home
│ ├── installation.md # Installation guide
│ ├── examples.md # Usage examples
│ ├── contributing.md # Contribution guidelines
│ ├── assets/ # Documentation assets
│ │ ├── pyCropWat.png # Logo image
│ │ ├── pyCropWat.gif # Animated logo
│ │ ├── pyCropWat_logo.png # Alternative logo
│ │ └── examples/ # Example output images for docs
│ │ ├── arizona/ # Arizona example figures
│ │ ├── comparisons/ # Dataset comparison figures
│ │ ├── figures/ # Rio de la Plata figures
│ │ ├── method_comparison/ # Method comparison figures
│ │ ├── new_mexico/ # New Mexico example figures
│ │ └── pcml/ # Western U.S. PCML example figures
│ ├── api/ # API reference
│ │ ├── analysis.md
│ │ ├── cli.md
│ │ ├── core.md
│ │ ├── methods.md
│ │ └── utils.md
│ └── user-guide/ # User guide
│ ├── api.md
│ ├── cli.md
│ └── quickstart.md
├── Examples/ # Example scripts and data
│ ├── README.md # Detailed workflow documentation
│ ├── south_america_example.py # Rio de la Plata workflow script
│ ├── arizona_example.py # Arizona workflow script
│ ├── new_mexico_example.py # New Mexico workflow script
│ ├── western_us_pcml_example.py # Western U.S. PCML workflow script
│ ├── ucrb_example.py # UCRB field-scale workflow script
│ ├── AZ.geojson # Arizona boundary GeoJSON
│ ├── NM.geojson # New Mexico boundary GeoJSON
├── .github/ # GitHub configuration
│ └── workflows/
│ ├── docs.yml # GitHub Pages deployment workflow
│ └── publish.yml # PyPI publishing workflow
├── CHANGELOG.md # Release notes
├── MANIFEST.in # PyPI package manifest
├── mkdocs.yml # MkDocs configuration
├── environment.yml # Conda environment file
├── pyproject.toml # Package configuration
├── requirements.txt # pip dependencies
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
Note: The Examples/ folder contains complete workflow scripts with detailed documentation in README.md.
south_america_example.py: A comprehensive Python script demonstrating the complete pyCropWat workflow including data processing, temporal aggregation, statistical analysis, visualization (including anomaly, climatology, and trend maps), and dataset comparison using real Rio de la Plata data.arizona_example.py: A U.S.-focused workflow demonstrating 8 Peff methods with GridMET/PRISM precipitation and SSURGO AWC for Arizona, with U.S. vs Global dataset comparisons (excludes PCML).new_mexico_example.py: A New Mexico workflow comparing 8 Peff methods using PRISM precipitation with SSURGO AWC and gridMET ETo (excludes PCML).AZ.geojson: Arizona boundary GeoJSON for local geometry support.NM.geojson: New Mexico boundary GeoJSON for local geometry support.
Note: Output rasters (~32 GB) are not included in the repository. Run the example scripts with a GEE project ID to generate them locally.
See the Complete Workflow Examples section below for details.
Changelog: See CHANGELOG.md for release notes and version history.
|
pyCropWat converts precipitation data from any GEE climate dataset into effective precipitation and effective precipitation fraction rasters. It supports:
|

|
pyCropWat supports multiple methods for calculating effective precipitation:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
cropwat |
CROPWAT method from FAO |
fao_aglw |
FAO/AGLW Dependable Rainfall (80% exceedance) |
fixed_percentage |
Simple fixed percentage method (configurable, default 70%) |
dependable_rainfall |
FAO Dependable Rainfall at specified probability level |
farmwest |
FarmWest method: Peff = (P - 5) × 0.75 |
usda_scs |
USDA-SCS method with AWC and ETo (requires GEE assets) |
suet |
TAGEM-SuET method: P - ETo with 75mm threshold (requires ETo asset) |
pcml |
Physics-Constrained ML (Western U.S. only, Jan 2000 - Sep 2024); no geometry = full Western U.S., or provide geometry to subset |
ensemble |
Ensemble mean of all methods except TAGEM-SuET and PCML - default (requires AWC and ETo assets) |
The effective precipitation is calculated using the CROPWAT method (Smith, 1992; Muratoglu et al., 2023):
- If precipitation ≤ 250 mm:
Peff = P × (125 - 0.2 × P) / 125 - If precipitation > 250 mm:
Peff = 0.1 × P + 125
The FAO Land and Water Division (AGLW) Dependable Rainfall formula from FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 33, based on 80% probability exceedance:
- If precipitation ≤ 70 mm:
Peff = max(0.6 × P - 10, 0) - If precipitation > 70 mm:
Peff = 0.8 × P - 24
A simple method assuming a constant fraction of precipitation is effective:
Peff = P × fwherefis the effectiveness fraction (default: 0.7 or 70%)
The FAO Dependable Rainfall method (same as FAO/AGLW) estimates rainfall at a given probability level (default 80%):
- If precipitation ≤ 70 mm:
Peff = max(0.6 × P - 10, 0) - If precipitation > 70 mm:
Peff = 0.8 × P - 24
A probability scaling factor is applied:
- 50% probability: ~1.3× base estimate (less conservative)
- 80% probability: 1.0× base estimate (default)
- 90% probability: ~0.9× base estimate (more conservative)
A simple empirical formula used by the FarmWest program:
Peff = max((P - 5) × 0.75, 0)
Assumes the first 5 mm is lost to interception/evaporation, and 75% of the remaining precipitation is effective.
Reference: FarmWest - Effective Precipitation
The USDA Soil Conservation Service method that accounts for soil water holding capacity and evaporative demand:
- Calculate soil storage depth:
d = AWC × MAD × rooting_depth(MAD = Maximum Allowable Depletion, default 0.5) - Calculate storage factor:
sf = 0.531747 + 0.295164×d - 0.057697×d² + 0.003804×d³ - Calculate effective precipitation:
Peff = sf × (P^0.82416 × 0.70917 - 0.11556) × 10^(ETo × 0.02426) - Peff is clamped between 0 and min(P, ETo)
Required GEE Assets:
| Region | AWC Asset | ETo Asset |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. | projects/openet/soil/ssurgo_AWC_WTA_0to152cm_composite |
projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 (band: eto) |
| Global | projects/sat-io/open-datasets/FAO/HWSD_V2_SMU (band: AWC) |
projects/climate-engine-pro/assets/ce-ag-era5-v2/daily (band: ReferenceET_PenmanMonteith_FAO56, use --eto-is-daily) |
CLI Example (U.S.):
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR --band total_precipitation_sum \
--gee-geometry projects/my-project/assets/study_area \
--start-year 2015 --end-year 2020 --scale-factor 1000 \
--method usda_scs \
--awc-asset projects/openet/soil/ssurgo_AWC_WTA_0to152cm_composite \
--eto-asset projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 \
--eto-band eto --rooting-depth 1.0 --mad-factor 0.5 --output ./outputCLI Example (Global):
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR --band total_precipitation_sum \
--gee-geometry projects/my-project/assets/study_area \
--start-year 2015 --end-year 2020 --scale-factor 1000 \
--method usda_scs \
--awc-asset projects/sat-io/open-datasets/FAO/HWSD_V2_SMU --awc-band AWC \
--eto-asset projects/climate-engine-pro/assets/ce-ag-era5-v2/daily \
--eto-band ReferenceET_PenmanMonteith_FAO56 --eto-is-daily \
--rooting-depth 1.0 --mad-factor 0.5 --output ./outputReference: USDA SCS (1993). Chapter 2 Irrigation Water Requirements. Part 623 National Engineering Handbook.
The TAGEM-SuET (Türkiye'de Sulanan Bitkilerin Bitki Su Tüketimleri - Turkish Irrigation Management and Plant Water Consumption System) method calculates effective precipitation based on the difference between precipitation and reference evapotranspiration:
- If P ≤ ETo:
Peff = 0 - If P > ETo and (P - ETo) < 75:
Peff = P - ETo - Otherwise:
Peff = 75 + 0.0011×(P - ETo - 75)² + 0.44×(P - ETo - 75)
⚠️ Note: Studies have shown that the TAGEM-SuET method tends to underperform compared to other methods, particularly in arid and semi-arid climates where ETo often exceeds precipitation. In our method comparison analyses, TAGEM-SuET consistently produced the lowest effective precipitation estimates. Users should consider this limitation when selecting a method for their application.
CLI Example:
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR --band total_precipitation_sum \
--gee-geometry projects/my-project/assets/study_area \
--start-year 2015 --end-year 2020 --scale-factor 1000 \
--method suet \
--eto-asset projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 \
--eto-band eto --output ./outputThe PCML method uses pre-computed effective precipitation from a physics-constrained machine learning model trained specifically for the Western United States. Unlike other methods, PCML Peff is retrieved directly from a GEE asset.
Coverage:
- Region: Western U.S. (17 states: AZ, CA, CO, ID, KS, MT, NE, NV, NM, ND, OK, OR, SD, TX, UT, WA, WY)
- Temporal: January 2000 - September 2024 (monthly)
- Resolution: ~2 km (native scale retrieved dynamically from GEE asset)
- GEE Asset:
projects/ee-peff-westus-unmasked/assets/effective_precip_monthly_unmasked - Band Format:
bYYYY_M(e.g.,b2015_9for September 2015,b2016_10for October 2016)
📝 Note: PCML provides pre-computed Peff values from a trained ML model. When using
--method pcml, the default PCML asset is automatically used and bands are dynamically selected based on the year/month being processed. The native scale (~2km) is retrieved from the asset using GEE'snominalScale()function. Only annual (water year, Oct-Sep) effective precipitation fractions are available for PCML, loaded directly from a separate GEE asset (projects/ee-peff-westus-unmasked/assets/effective_precip_fraction_unmasked, WY 2000-2024, band format:bYYYY).
💡 PCML Geometry Options:
- No geometry provided: Downloads the entire PCML asset (full Western U.S. - 17 states)
- User provides geometry: PCML data is clipped/subsetted to that geometry. Note: Only Western U.S. vectors that overlap with the 17-state extent can be used (e.g., AZ.geojson, pacific_northwest.geojson)
CLI Example (full Western U.S.):
pycropwat process \
--method pcml \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2024 \
--output ./WesternUS_PCMLCLI Example (subset to specific region):
pycropwat process \
--method pcml \
--geometry pacific_northwest.geojson \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2024 \
--output ./PacificNW_PCMLThe ensemble method provides a robust estimate by calculating the mean of all methods except TAGEM-SuET and PCML. The ensemble includes:
- CROPWAT - FAO standard method
- FAO/AGLW - Dependable Rainfall (80% exceedance)
- Fixed Percentage - 70% of precipitation
- Dependable Rainfall - 75% probability level
- FarmWest - Pacific Northwest method
- USDA-SCS - Soil-based method
Formula: Peff_ensemble = (Peff_cropwat + Peff_fao_aglw + Peff_fixed + Peff_dependable + Peff_farmwest + Peff_usda_scs) / 6
💡 Note: The ensemble method requires AWC and ETo assets (same as USDA-SCS) since it internally calculates all component methods. This method is recommended when users want a robust, multi-method average that reduces bias from any single method.
CLI Example:
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR --band total_precipitation_sum \
--gee-geometry projects/my-project/assets/study_area \
--start-year 2015 --end-year 2020 --scale-factor 1000 \
--method ensemble \
--awc-asset projects/sat-io/open-datasets/FAO/HWSD_V2_SMU --awc-band AWC \
--eto-asset projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 \
--eto-band eto --output ./output| Method | Use Case | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| CROPWAT | General irrigation planning | Balanced, widely validated |
| FAO/AGLW | Yield response studies | FAO Dependable Rainfall (80% exceedance) |
| Fixed Percentage | Quick estimates, calibration | Simple, requires local calibration |
| Dependable Rainfall | Risk-averse planning | Same as FAO/AGLW, with probability scaling |
| FarmWest | Pacific Northwest irrigation | Simple, accounts for interception loss |
| USDA-SCS | Site-specific irrigation planning | Accounts for soil AWC and ETo |
| TAGEM-SuET | ET-based irrigation planning | Based on P - ETo difference |
| PCML | Western U.S. applications | ML-based, pre-computed (2000-2024) |
| Ensemble | Robust multi-method estimate | Mean of 6 methods (excludes TAGEM-SuET and PCML) |
pip install pycropwatOr with optional interactive map support:
pip install pycropwat[interactive]| Component | Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Repository (tracked files) | ~50 MB | Core package, documentation, examples, and assets |
| Generated by example scripts: | ||
| Examples/RioDelaPlata | ~5 GB | ERA5-Land & TerraClimate outputs (2000-2025) |
| Examples/Arizona | ~12 GB | GridMET, PRISM, ERA5-Land & TerraClimate outputs (1985-2025) |
| Examples/NewMexico | ~8 GB | PRISM 8-method outputs (1986-2025) |
| Examples/WesternUS_PCML | ~3 GB | PCML effective precipitation outputs |
| Examples/UCRB | ~3 MB | Field-scale analysis outputs |
Note: Large generated data files are excluded from the repository via .gitignore.
Run the example scripts to generate them locally:
python Examples/south_america_example.py --gee-project your-project-id
python Examples/arizona_example.py --gee-project your-project-id
python Examples/new_mexico_example.py --gee-project your-project-id
python Examples/western_us_pcml_example.py --gee-project your-project-id
python Examples/ucrb_example.py --gee-project your-project-id
⚠️ UCRB GeoPackage: Theucrb_field_effective_precip_intercomparison_geopackage.gpkgfile (~7 GB) is not included in the repository. Contact the authors if you need access to this dataset.
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/montimaj/pyCropWat.git
cd pyCropWat
# Create conda environment from environment.yml
conda env create -f environment.yml
# Activate the environment
conda activate pycropwat
# Install the package (registers the 'pycropwat' CLI command)
pip install -e .
# Or with interactive map support (leafmap, localtileserver)
pip install -e ".[interactive]"
# Verify installation
pycropwat --help# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/montimaj/pyCropWat.git
cd pyCropWat
# Create and activate a virtual environment (optional but recommended)
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
# Install the package (registers the 'pycropwat' CLI command)
pip install -e .
# Or with interactive map support (leafmap, localtileserver)
pip install -e ".[interactive]"
# Verify installation
pycropwat --helpNote: After running pip install -e ., the pycropwat command will be available globally in your environment. Do not use ./pycropwat - just use pycropwat directly.
Optional Dependencies:
pip install -e ".[interactive]"- Adds leafmap and localtileserver for interactive HTML mapspip install -e ".[dev]"- Adds development tools (pytest, black, ruff)pip install -e ".[docs]"- Adds documentation tools (mkdocs)
## Requirements
- Python >= 3.9
- Google Earth Engine account and authentication
- Dependencies: earthengine-api, numpy, xarray, rioxarray, geopandas, shapely, dask
### Conda Environment
The `environment.yml` file provides a complete conda environment with all dependencies:
```bash
# Create environment
conda env create -f environment.yml
# Activate environment
conda activate pycropwat
# Update existing environment
conda env update -f environment.yml --prune
# Remove environment
conda env remove -n pycropwat
from pycropwat import EffectivePrecipitation
# Initialize the processor with a local file
ep = EffectivePrecipitation(
asset_id='ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR',
precip_band='total_precipitation_sum',
geometry_path='path/to/region.geojson',
start_year=2015,
end_year=2020,
precip_scale_factor=1000, # ERA5 precipitation is in meters, convert to mm
gee_project='your-gee-project' # Optional
)
# Or use a GEE FeatureCollection asset for the study area
ep = EffectivePrecipitation(
asset_id='ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR',
precip_band='total_precipitation_sum',
gee_geometry_asset='projects/my-project/assets/study_boundary',
start_year=2015,
end_year=2020,
precip_scale_factor=1000
)
# Use alternative effective precipitation methods
ep = EffectivePrecipitation(
asset_id='ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR',
precip_band='total_precipitation_sum',
gee_geometry_asset='projects/my-project/assets/study_boundary',
start_year=2015,
end_year=2020,
precip_scale_factor=1000,
method='fao_aglw' # Options: 'cropwat', 'fao_aglw', 'fixed_percentage', 'dependable_rainfall', 'farmwest', 'usda_scs', 'suet', 'ensemble'
)
# Process with parallel execution (using dask)
results = ep.process(
output_dir='./output',
n_workers=4,
months=[6, 7, 8] # Optional: process only specific months
)
# Or process sequentially (useful for debugging)
results = ep.process_sequential(output_dir='./output')from pycropwat import TemporalAggregator, StatisticalAnalyzer, Visualizer
# Temporal aggregation
agg = TemporalAggregator('./output')
# Annual total
annual = agg.annual_aggregate(2020, method='sum', output_path='./annual_2020.tif')
# Seasonal aggregate (JJA = June-July-August)
summer = agg.seasonal_aggregate(2020, 'JJA', method='sum')
# Growing season - Northern Hemisphere (April-October, same year)
growing_nh = agg.growing_season_aggregate(2020, start_month=4, end_month=10)
# Growing season - Southern Hemisphere (October-March, cross-year)
# Aggregates Oct 2020 - Mar 2021 when start_month > end_month
growing_sh = agg.growing_season_aggregate(2020, start_month=10, end_month=3)
# Multi-year climatology
climatology = agg.multi_year_climatology(2000, 2020, output_dir='./climatology')
# Statistical analysis
stats = StatisticalAnalyzer('./output')
# Calculate anomaly
anomaly = stats.calculate_anomaly(2020, 6, clim_start=1990, clim_end=2020,
anomaly_type='percent')
# Trend analysis (returns slope in mm/year and p-value)
slope, pvalue = stats.calculate_trend(start_year=2000, end_year=2020, month=6)
# Zonal statistics
zonal_df = stats.zonal_statistics('./zones.shp', 2000, 2020, output_path='./zonal_stats.csv')
# Visualization
viz = Visualizer('./output')
viz.plot_time_series(2000, 2020, output_path='./timeseries.png')
viz.plot_monthly_climatology(2000, 2020, output_path='./climatology.png')
viz.plot_raster(2020, 6, output_path='./map_2020_06.png')
# Interactive map (requires leafmap or folium: pip install leafmap)
viz.plot_interactive_map(2020, 6, output_path='./interactive_map.html')
# Dataset comparison
viz.plot_comparison(2020, 6, other_dir='./terraclimate_output',
labels=('ERA5', 'TerraClimate'), output_path='./comparison.png')
viz.plot_scatter_comparison(2000, 2020, other_dir='./terraclimate_output',
labels=('ERA5', 'TerraClimate'), output_path='./scatter.png')
viz.plot_annual_comparison(2000, 2020, other_dir='./terraclimate_output',
labels=('ERA5', 'TerraClimate'), output_path='./annual_comparison.png')from pycropwat import export_to_netcdf, export_to_cog
# Export to NetCDF (single file with time dimension)
export_to_netcdf('./output', './effective_precip.nc')
# Convert to Cloud-Optimized GeoTIFF
export_to_cog('./output/effective_precip_2020_06.tif', './cog_2020_06.tif')pyCropWat provides a subcommand-based CLI for all functionality:
pycropwat <command> [OPTIONS]Available Commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
process |
Calculate effective precipitation from GEE climate data |
aggregate |
Temporal aggregation (annual, seasonal, growing season) |
analyze |
Statistical analysis (anomaly, trend, zonal statistics) |
export |
Export to NetCDF or Cloud-Optimized GeoTIFF |
plot |
Create visualizations (time series, climatology, maps) |
# Process ERA5-Land data (actual working example)
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR \
--band total_precipitation_sum \
--gee-geometry projects/ssebop-471916/assets/Riodelaplata \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2025 \
--scale-factor 1000 --scale 4000 \
--workers 32 --output ./Examples/RioDelaPlata/RDP_ERA5Land
# Use alternative effective precipitation method
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR \
--band total_precipitation_sum \
--gee-geometry projects/my-project/assets/study_area \
--start-year 2020 --end-year 2023 \
--scale-factor 1000 \
--method fao_aglw --output ./outputs
# List available methods
pycropwat --list-methods
# Process TerraClimate data (actual working example)
pycropwat process --asset IDAHO_EPSCOR/TERRACLIMATE \
--band pr \
--gee-geometry projects/ssebop-471916/assets/Riodelaplata \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2025 \
--workers 32 --output ./Examples/RioDelaPlata/RDP_TerraClimate
# Process with local shapefile
pycropwat process --asset ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR \
--band total_precipitation_sum \
--geometry roi.geojson \
--start-year 2015 --end-year 2020 \
--scale-factor 1000 --output ./output# Annual total
pycropwat aggregate --input ./output --type annual --year 2020 --output ./annual_2020.tif
# Seasonal (summer)
pycropwat aggregate --input ./output --type seasonal --year 2020 --season JJA --output ./summer_2020.tif
# Growing season (April-October)
pycropwat aggregate --input ./output --type growing-season --year 2020 \
--start-month 4 --end-month 10 --output ./growing_2020.tif
# Multi-year climatology
pycropwat aggregate --input ./output --type climatology \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 --output ./climatology/# Calculate anomaly
pycropwat analyze anomaly --input ./output --year 2020 --month 6 \
--clim-start 1990 --clim-end 2020 --output ./anomaly_2020_06.tif
# Calculate trend
pycropwat analyze trend --input ./output --start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 \
--trend-method sen --output ./trend/
# Zonal statistics
pycropwat analyze zonal --input ./output --zones ./regions.shp \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 --output ./zonal_stats.csv# Export to NetCDF
pycropwat export netcdf --input ./output --output ./data.nc
# Convert to Cloud-Optimized GeoTIFF
pycropwat export cog --input ./effective_precip_2020_06.tif --output ./cog_2020_06.tif# Time series plot
pycropwat plot timeseries --input ./output --start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 --output ./timeseries.png
# Monthly climatology bar chart
pycropwat plot climatology --input ./output --start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 --output ./climatology.png
# Single month map
pycropwat plot map --input ./output --year 2020 --month 6 --output ./map_2020_06.png
# Interactive map (requires leafmap: pip install leafmap)
pycropwat plot interactive --input ./output --year 2020 --month 6 --output ./map.html
# Compare two datasets (e.g., ERA5 vs TerraClimate)
pycropwat plot compare --input ./era5_output --other-input ./terraclimate_output \
--year 2020 --month 6 --label1 ERA5 --label2 TerraClimate \
--output ./comparison.png
# Scatter plot for validation
pycropwat plot scatter --input ./era5_output --other-input ./terraclimate_output \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 --output ./scatter.png
# Annual comparison bar chart
pycropwat plot annual-compare --input ./era5_output --other-input ./terraclimate_output \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2020 --output ./annual.png| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
--help |
Show help message |
--version |
Show version number |
--list-methods |
List available effective precipitation methods |
| Argument | Short | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
--asset |
-a |
Yes | - | GEE ImageCollection asset ID |
--band |
-b |
Yes | - | Precipitation band name |
--geometry |
-g |
No* | - | Path to shapefile or GeoJSON |
--gee-geometry |
-G |
No* | - | GEE FeatureCollection asset ID |
--start-year |
-s |
Yes | - | Start year (inclusive) |
--end-year |
-e |
Yes | - | End year (inclusive) |
--output |
-o |
Yes | - | Output directory |
--scale-factor |
-f |
No | 1.0 | Conversion factor to mm |
--scale |
-r |
No | Native | Output resolution in meters |
--workers |
-w |
No | 4 | Number of parallel workers |
--months |
-m |
No | All | Specific months to process |
--project |
-p |
No | None | GEE project ID |
--method |
- | No | ensemble | Peff method: cropwat, fao_aglw, fixed_percentage, dependable_rainfall, farmwest, usda_scs, suet, ensemble |
--percentage |
- | No | 0.7 | Percentage for fixed_percentage method |
--probability |
- | No | 0.75 | Probability for dependable_rainfall method |
--sequential |
- | No | False | Process sequentially |
--verbose |
-v |
No | False | Verbose output |
* Either --geometry or --gee-geometry must be provided.
For full CLI documentation, run pycropwat <command> --help or see the CLI Reference.
The package generates two GeoTIFF files per month:
effective_precip_YYYY_MM.tif- Effective precipitation (mm)effective_precip_fraction_YYYY_MM.tif- Effective precipitation fraction (0-1)
Note: For the PCML method, fraction files are annual (water year):
effective_precip_fraction_YYYY.tif(one per year, WY 2000-2024).
- Default (no
--scale): Uses the native resolution of the input dataset- ERA5-Land: ~11 km (0.1°)
- TerraClimate: ~4 km (1/24°)
- CHIRPS: ~5.5 km (0.05°)
- With
--scale: Reprojects to the specified resolution in meters (e.g.,--scale 1000for 1 km)
For large study areas or high-resolution outputs that exceed GEE's pixel limits (262,144 pixels per request), pyCropWat automatically:
- Estimates pixel count for the region
- Splits large regions into smaller tiles (max 256×256 pixels per tile)
- Downloads each tile separately from GEE
- Mosaics the tiles back together in memory (no temp files)
- Resizes to match the target resolution
This applies to precipitation, AWC, and ETo data downloads. No configuration required - it's handled automatically.
The CROPWAT formula is calibrated for precipitation in millimeters (mm). The output effective precipitation is always in mm, provided you use the correct --scale-factor to convert input precipitation to mm first.
The formula constants (125, 250, 0.2, 0.1) are specifically designed for mm units:
- If P ≤ 250mm:
Peff = P × (125 - 0.2 × P) / 125 - If P > 250mm:
Peff = 0.1 × P + 125
Warning: If you pass precipitation in wrong units (e.g., ERA5 in meters without --scale-factor 1000), the results will be incorrect because the 250mm threshold won't match properly.
pyCropWat automatically sums all images within each month to compute monthly total precipitation, regardless of the input data's temporal resolution:
- Monthly data (ERA5, TerraClimate): Uses the single monthly image directly
- Daily data (CHIRPS/DAILY): Sums all ~30 daily images → monthly total
- Sub-daily data (GPM IMERG): Sums all timesteps → monthly total
This ensures the CROPWAT formula always receives the correct monthly precipitation totals.
| Asset ID | Precipitation Band | Scale Factor | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ECMWF/ERA5_LAND/MONTHLY_AGGR |
total_precipitation_sum |
1000 | ~11 km (0.1°) | Monthly |
ECMWF/ERA5/MONTHLY |
total_precipitation |
1000 | ~27 km (0.25°) | Monthly |
IDAHO_EPSCOR/TERRACLIMATE |
pr |
1 | ~4 km (1/24°) | Monthly |
UCSB-CHG/CHIRPS/DAILY |
precipitation |
1 | ~5.5 km (0.05°) | Daily |
UCSB-CHG/CHIRPS/PENTAD |
precipitation |
1 | ~5.5 km (0.05°) | 5-day (Pentad) |
NASA/GPM_L3/IMERG_V06 |
precipitation |
1 | ~11 km (0.1°) | Half-hourly |
projects/climate-engine-pro/assets/ce-ag-era5-v2/daily |
Precipitation_Flux |
1 | ~9 km (0.1°) | Daily |
| Asset ID | Precipitation Band | Scale Factor | Spatial Resolution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IDAHO_EPSCOR/GRIDMET |
pr |
1 | ~4 km | University of Idaho GridMET daily meteorological data |
projects/sat-io/open-datasets/OREGONSTATE/PRISM_800_MONTHLY |
ppt |
1 | ~800 m | Oregon State PRISM high-resolution monthly precipitation |
For the USDA-SCS method, you need AWC (Available Water Capacity) and ETo (Reference ET) data:
| Region | Dataset Type | Asset ID | Band | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. | AWC | projects/openet/soil/ssurgo_AWC_WTA_0to152cm_composite |
(single band) | SSURGO soil data |
| U.S. | ETo | projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 |
eto |
GridMET monthly ETo |
| Global | AWC | projects/sat-io/open-datasets/FAO/HWSD_V2_SMU |
AWC |
FAO HWSD v2 |
| Global | ETo | projects/climate-engine-pro/assets/ce-ag-era5-v2/daily |
ReferenceET_PenmanMonteith_FAO56 |
ERA5-based (use --eto-is-daily) |
The Examples/ directory contains comprehensive workflow scripts demonstrating pyCropWat capabilities:
📖 Script: Examples/south_america_example.py
Demonstrates the complete pyCropWat workflow comparing ERA5-Land and TerraClimate data for South America.
For detailed step-by-step documentation, see Examples/README.md
The script performs a comprehensive 6-step workflow:
- Process Effective Precipitation - Downloads and calculates effective precipitation from ERA5-Land and TerraClimate via GEE
- Temporal Aggregation - Creates annual totals, growing season aggregations (Apr-Sep), and monthly climatology
- Statistical Analysis - Computes percent anomalies, trends (Sen's slope), and zonal statistics
- Visualization - Generates time series plots, climatology charts, static maps, and interactive HTML maps
- Dataset Comparison - Creates side-by-side comparison plots, scatter plots, annual charts, and zonal comparisons
- NetCDF Export - Exports data to CF-compliant NetCDF format
# Navigate to the Examples directory
cd Examples/
# Run analysis only (using existing pre-processed data)
python south_america_example.py --analysis-only
# Run full workflow with GEE processing (requires authentication)
python south_america_example.py --gee-project your-project-id --workers 8
# Force reprocess all data from GEE
python south_america_example.py --force-reprocess --gee-project your-project-id --workers 8| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Area | Rio de la Plata Basin (GEE Asset: projects/ssebop-471916/assets/Riodelaplata) |
| Time Period | 2000-2025 |
| Climatology Period | 2000-2020 |
| Datasets | ERA5-Land, TerraClimate |
| Sample Zones | Eastern RDP (Uruguay, SE Brazil), Western RDP (N Argentina, Paraguay) |
📖 Script: Examples/arizona_example.py
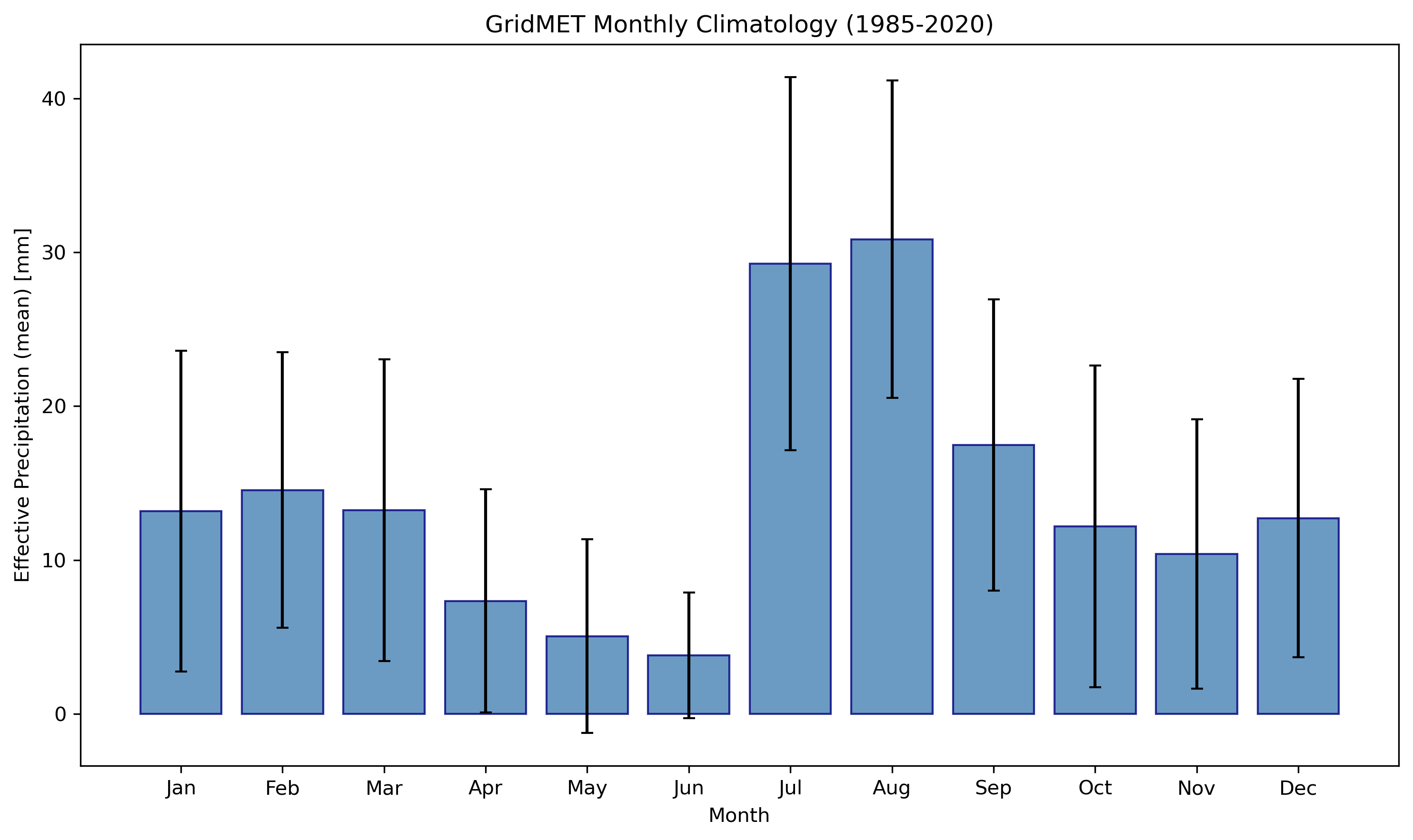
Demonstrates the USDA-SCS method with U.S.-specific AWC and ETo datasets for Arizona, comparing GridMET and PRISM precipitation data.
The Arizona example uses these U.S.-based GEE datasets:
| Dataset | GEE Asset ID | Band |
|---|---|---|
| Precipitation (GridMET) | IDAHO_EPSCOR/GRIDMET |
pr |
| Precipitation (PRISM) | projects/sat-io/open-datasets/OREGONSTATE/PRISM_800_MONTHLY |
ppt |
| AWC (SSURGO) | projects/openet/soil/ssurgo_AWC_WTA_0to152cm_composite |
(single band) |
| ETo (GridMET) | projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 |
eto |
- Process Effective Precipitation - Uses USDA-SCS method with SSURGO AWC and GridMET ETo
- Compare Precipitation Sources - GridMET (~4km) vs PRISM (~800m)
- Arizona-Specific Aggregation - Monsoon season (Jul-Sep), winter season (Jan-Feb)
- Zonal Statistics - Central AZ, Southern AZ, Northern AZ regions
- Dataset Comparison - GridMET vs PRISM scatter plots, zonal comparisons
cd Examples/
# Run analysis only (if data already processed)
python arizona_example.py --analysis-only
# Run full workflow with GEE processing
python arizona_example.py --gee-project your-project-id --workers 8
# Force reprocess
python arizona_example.py --force-reprocess --gee-project your-project-id# Process with GridMET precipitation using USDA-SCS method
pycropwat process --asset IDAHO_EPSCOR/GRIDMET --band pr \
--gee-geometry users/montimajumdar/AZ \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2024 --scale 4000 \
--method usda_scs \
--awc-asset projects/openet/soil/ssurgo_AWC_WTA_0to152cm_composite \
--eto-asset projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 \
--eto-band eto --rooting-depth 1.0 --mad-factor 0.5 \
--workers 8 --output ./AZ_GridMET_USDA_SCS
# Process with PRISM precipitation
pycropwat process --asset projects/sat-io/open-datasets/OREGONSTATE/PRISM_800_MONTHLY --band ppt \
--gee-geometry users/montimajumdar/AZ \
--start-year 2000 --end-year 2024 --scale 4000 \
--method usda_scs \
--awc-asset projects/openet/soil/ssurgo_AWC_WTA_0to152cm_composite \
--eto-asset projects/openet/assets/reference_et/conus/gridmet/monthly/v1 \
--eto-band eto --rooting-depth 1.0 --mad-factor 0.5 \
--workers 8 --output ./AZ_PRISM_USDA_SCS| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Study Area | Arizona (GEE Asset: users/montimajumdar/AZ) |
| Time Period | 2000-2024 |
| Climatology Period | 2000-2020 |
| Precipitation Datasets | GridMET, PRISM |
| AWC Dataset | SSURGO (OpenET) |
| ETo Dataset | GridMET Monthly (OpenET) |
| Rooting Depth | 1.0 m |
| MAD Factor | 0.5 (Management Allowed Depletion) |
| Sample Zones | Central AZ (Phoenix), Southern AZ (Tucson), Northern AZ (Flagstaff) |
Running the example creates organized outputs:
Examples/
├── south_america_example.py # Rio de la Plata workflow script
├── arizona_example.py # Arizona workflow script
├── new_mexico_example.py # New Mexico workflow script
├── AZ.geojson # Arizona boundary GeoJSON
├── NM.geojson # New Mexico boundary GeoJSON
├── README.md # Detailed documentation
├── RioDelaPlata/ # Rio de la Plata region
│ ├── RDP_ERA5Land/ # Monthly effective precipitation (ERA5-Land)
│ │ ├── effective_precip_YYYY_MM.tif
│ │ └── effective_precip_fraction_YYYY_MM.tif
│ ├── RDP_TerraClimate/ # Monthly effective precipitation (TerraClimate)
│ │ ├── effective_precip_YYYY_MM.tif
│ │ └── effective_precip_fraction_YYYY_MM.tif
│ ├── analysis_inputs/ # Downloaded input data
│ │ ├── RDP_ERA5Land/
│ │ │ └── precip_YYYY_MM.tif
│ │ └── RDP_TerraClimate/
│ │ └── precip_YYYY_MM.tif
│ └── analysis_outputs/
│ ├── annual/ # Annual totals by dataset
│ │ ├── ERA5Land/
│ │ └── TerraClimate/
│ ├── climatology/ # Monthly climatology (2000-2020)
│ │ ├── ERA5Land/
│ │ │ └── climatology_2000_2020_month_MM.tif
│ │ └── TerraClimate/
│ ├── anomalies/ # Percent anomalies
│ │ ├── ERA5Land/
│ │ │ └── anomaly_YYYY_MM.tif
│ │ └── TerraClimate/
│ ├── trend/ # Trend analysis
│ │ ├── ERA5Land/
│ │ │ ├── trend_slope_2000_2025_annual.tif
│ │ │ └── trend_pvalue_2000_2025_annual.tif
│ │ └── TerraClimate/
│ ├── figures/ # Visualizations by dataset
│ │ ├── ERA5Land/
│ │ │ ├── time_series.png
│ │ │ ├── monthly_climatology.png
│ │ │ ├── anomaly_map_YYYY_MM.png
│ │ │ ├── climatology_map_MM.png
│ │ │ ├── trend_maps.png
│ │ │ └── trend_map_with_significance.png
│ │ └── TerraClimate/
│ ├── comparisons/ # Dataset comparisons
│ └── method_comparison/ # Peff method comparison
└── Arizona/ # Arizona region
├── AZ_GridMET_USDA_SCS/ # GridMET U.S. dataset
│ ├── effective_precip_YYYY_MM.tif
│ └── effective_precip_fraction_YYYY_MM.tif
├── AZ_PRISM_USDA_SCS/ # PRISM U.S. dataset
├── AZ_ERA5Land_USDA_SCS/ # ERA5-Land global dataset
├── AZ_TerraClimate_USDA_SCS/ # TerraClimate global dataset
├── analysis_inputs/ # Downloaded input data (precip, AWC, ETo)
│ ├── AZ_GridMET_USDA_SCS/
│ │ ├── precip_YYYY_MM.tif
│ │ ├── awc.tif
│ │ └── eto_YYYY_MM.tif
│ └── ... # Other datasets
└── analysis_outputs/
├── annual/
├── climatology/
│ └── {dataset}/
│ └── climatology_1985_2020_month_MM.tif
├── anomalies/
│ └── {dataset}/
│ └── anomaly_YYYY_MM.tif
├── trend/
│ └── {dataset}/
│ ├── trend_slope_1985_2025_annual.tif
│ └── trend_pvalue_1985_2025_annual.tif
├── figures/
│ └── {dataset}/
│ ├── time_series.png
│ ├── monthly_climatology.png
│ ├── anomaly_map_YYYY_MM.png
│ ├── climatology_map_MM.png
│ ├── trend_maps.png
│ └── trend_map_with_significance.png
├── comparisons/
├── us_vs_global/ # U.S. vs Global dataset comparison
└── method_comparison/ # All 6 Peff methods comparison
The following visualizations are generated by the complete workflow example using real Rio de la Plata basin data:
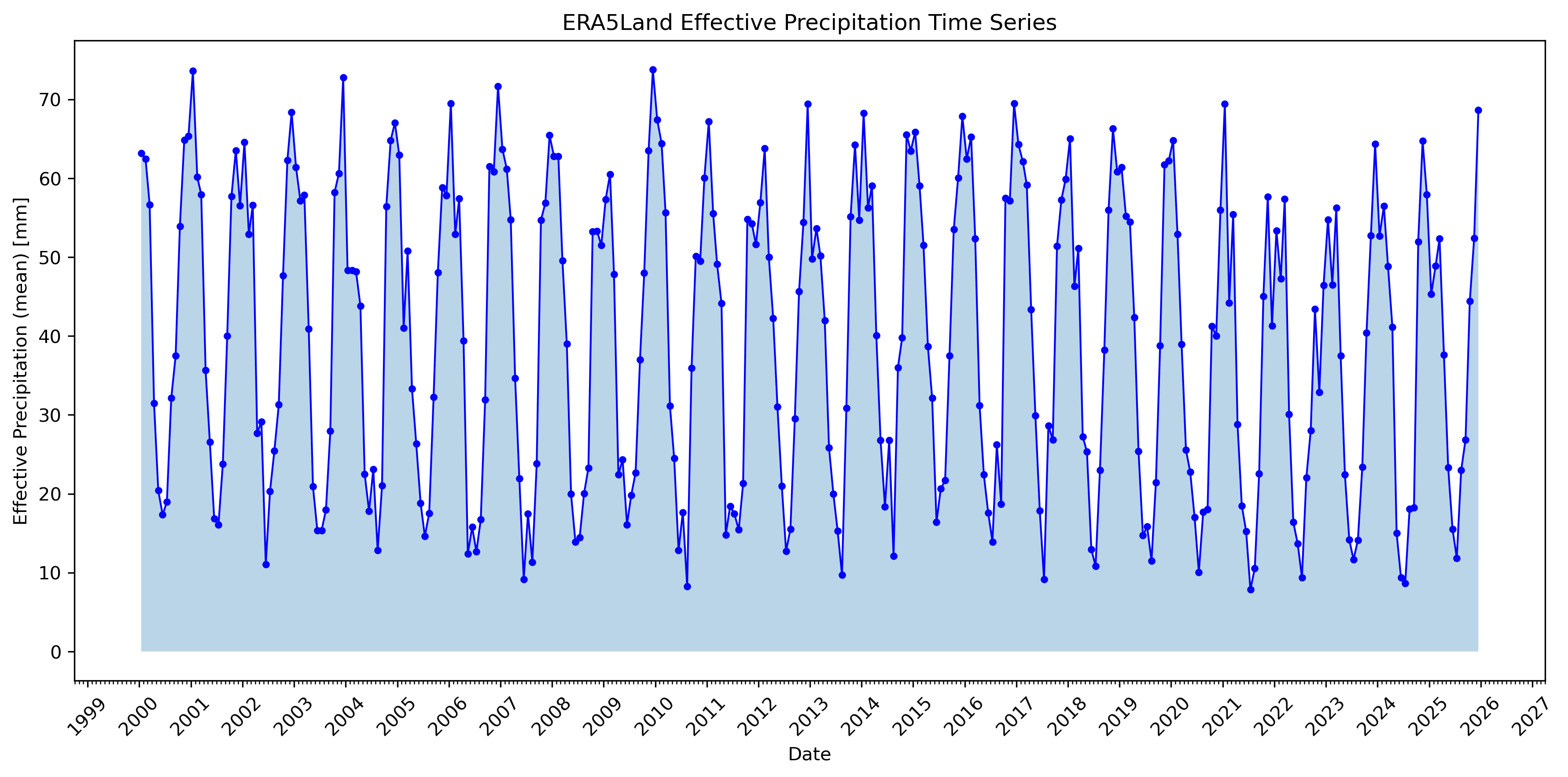
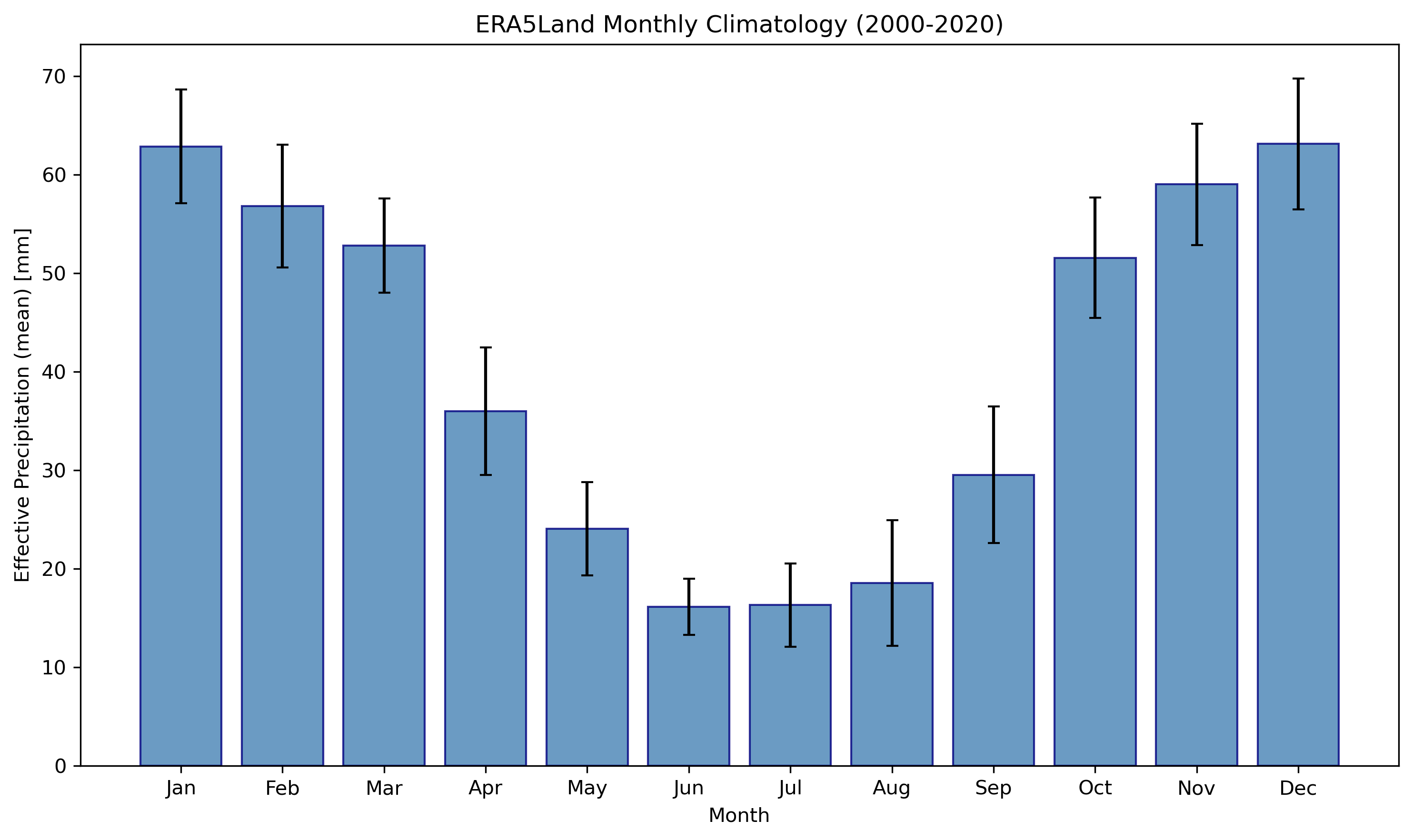
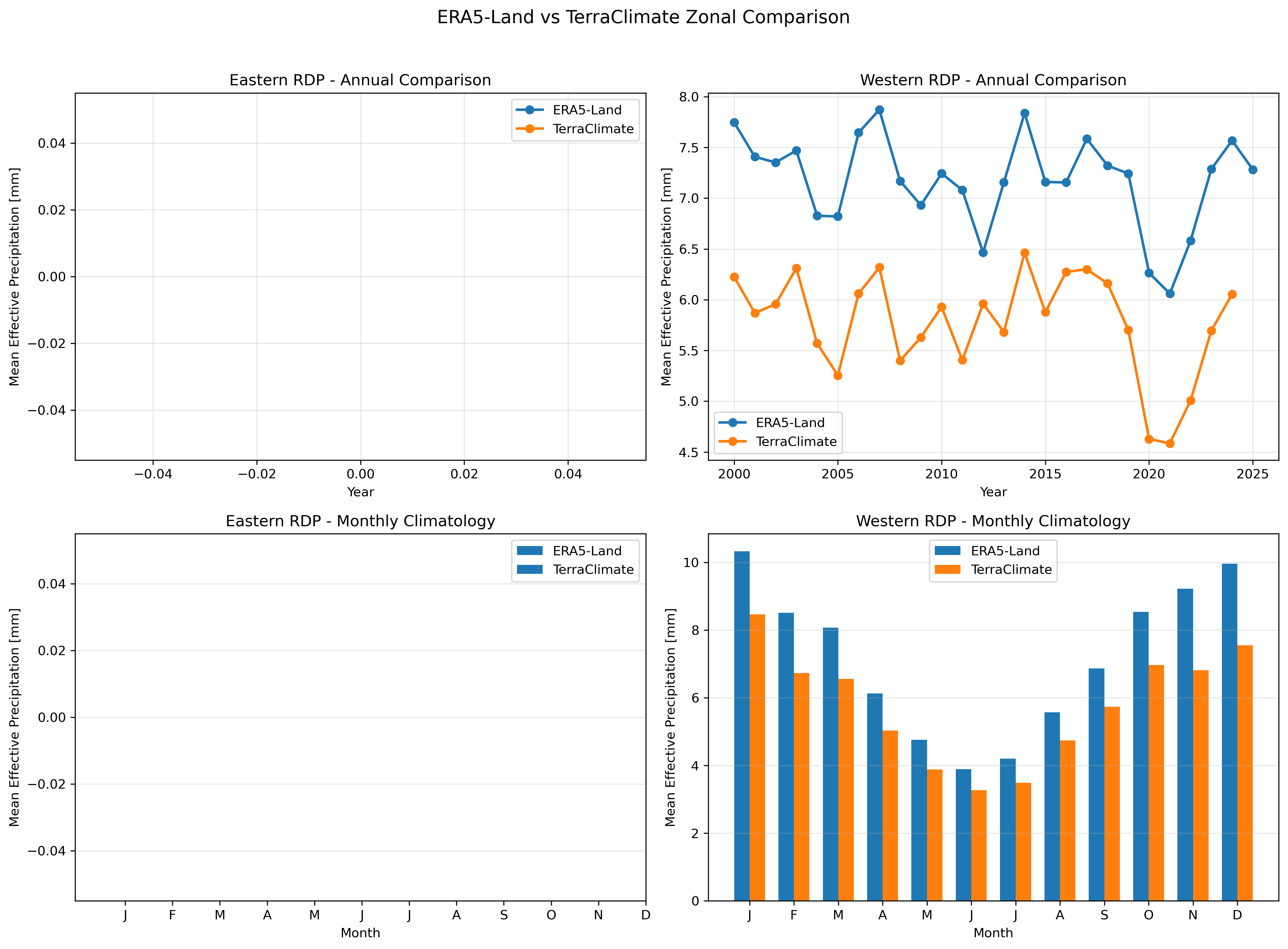
Left: Monthly effective precipitation time series (2000-2025). Right: Monthly climatology showing seasonal patterns.
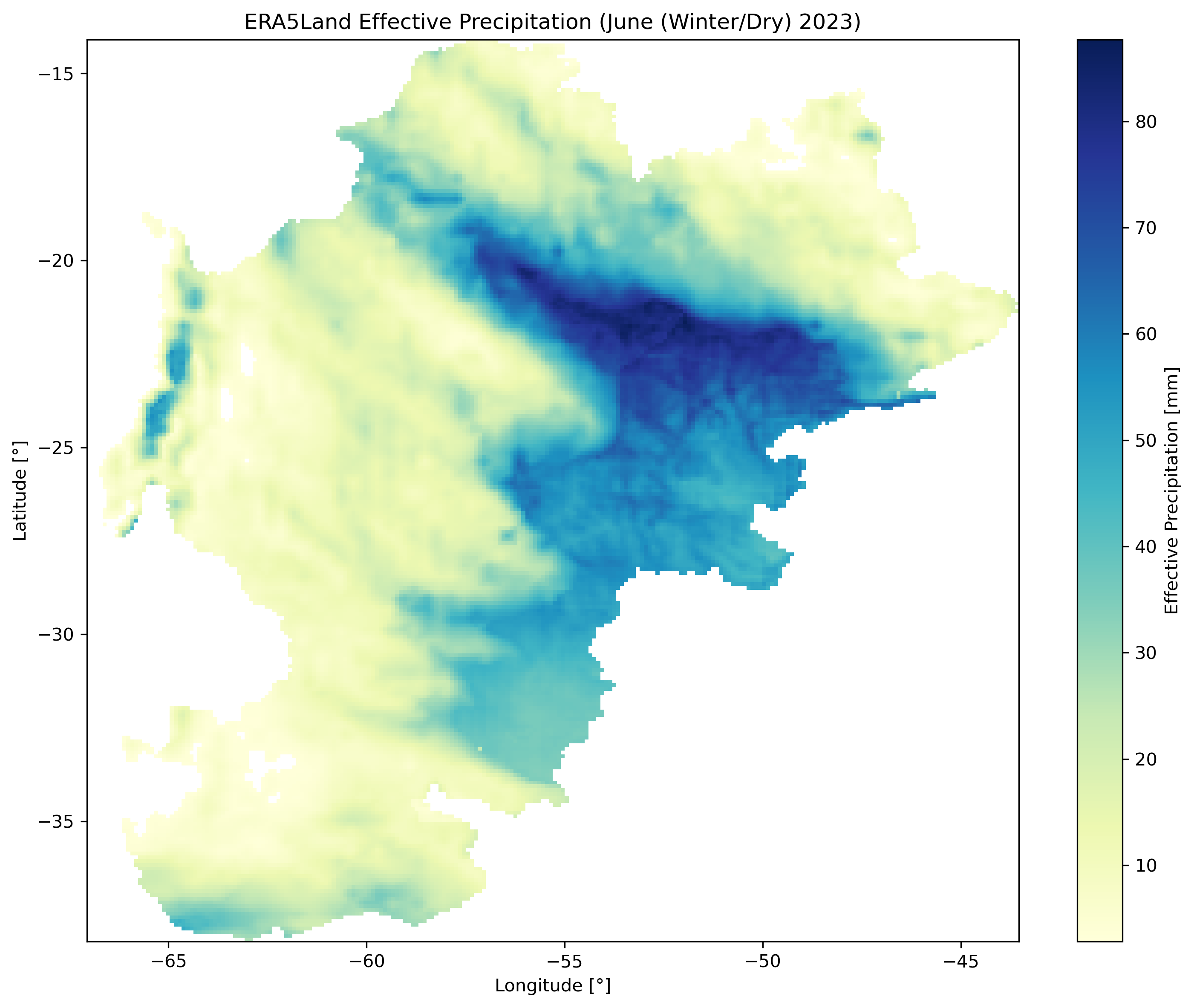
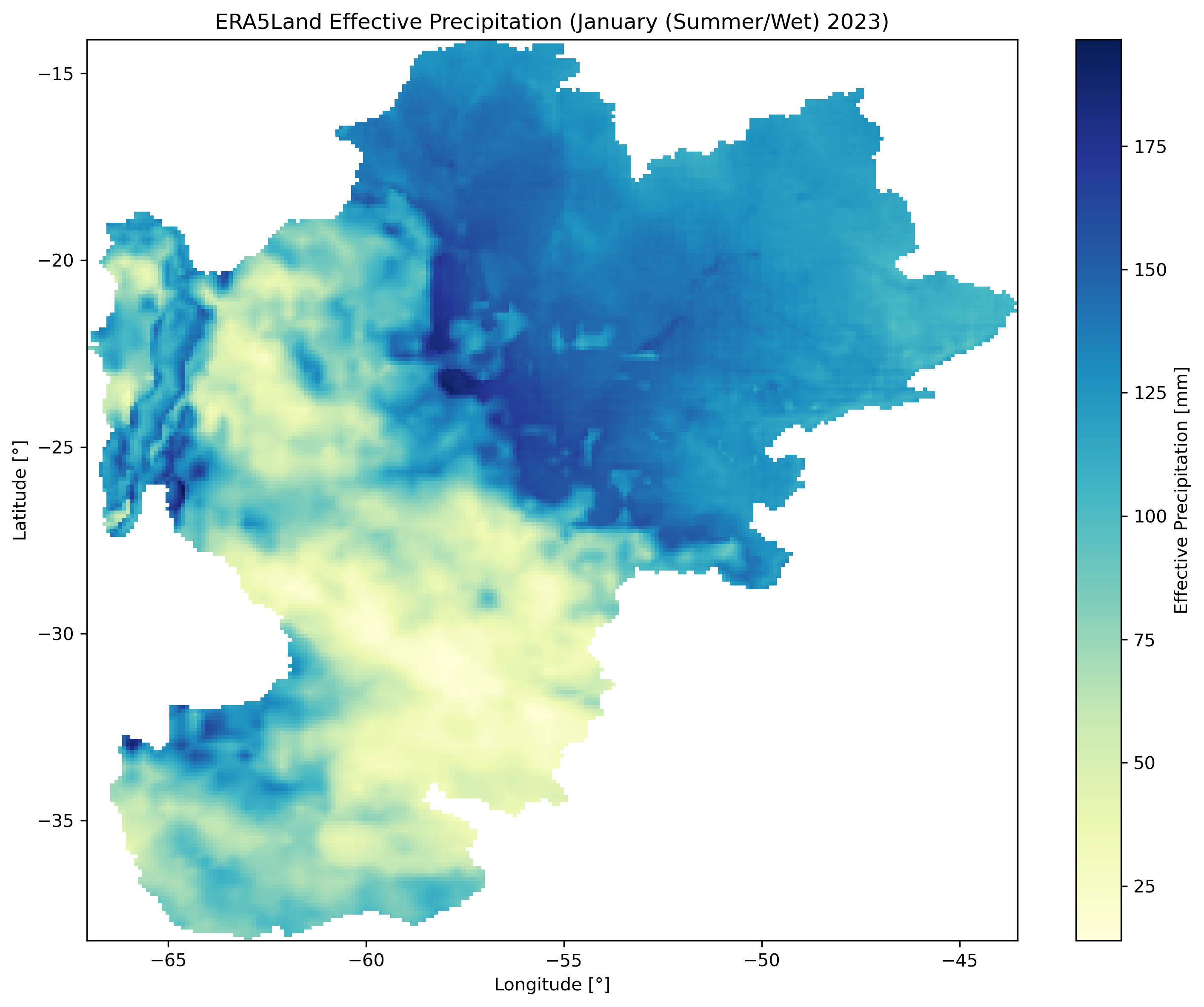
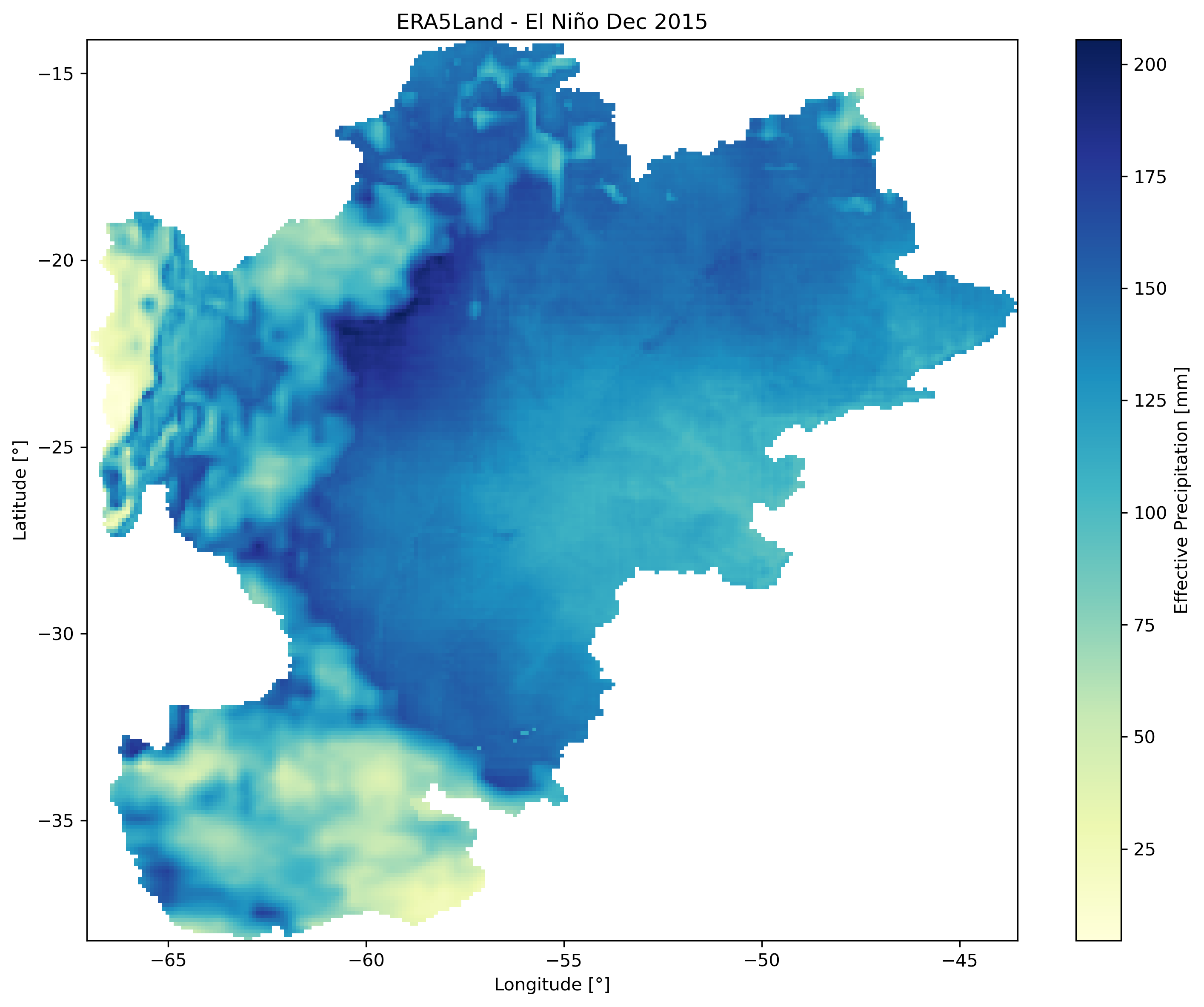
Left: Winter dry season (June 2023). Center: Summer wet season (January 2023). Right: El Niño event (December 2015).
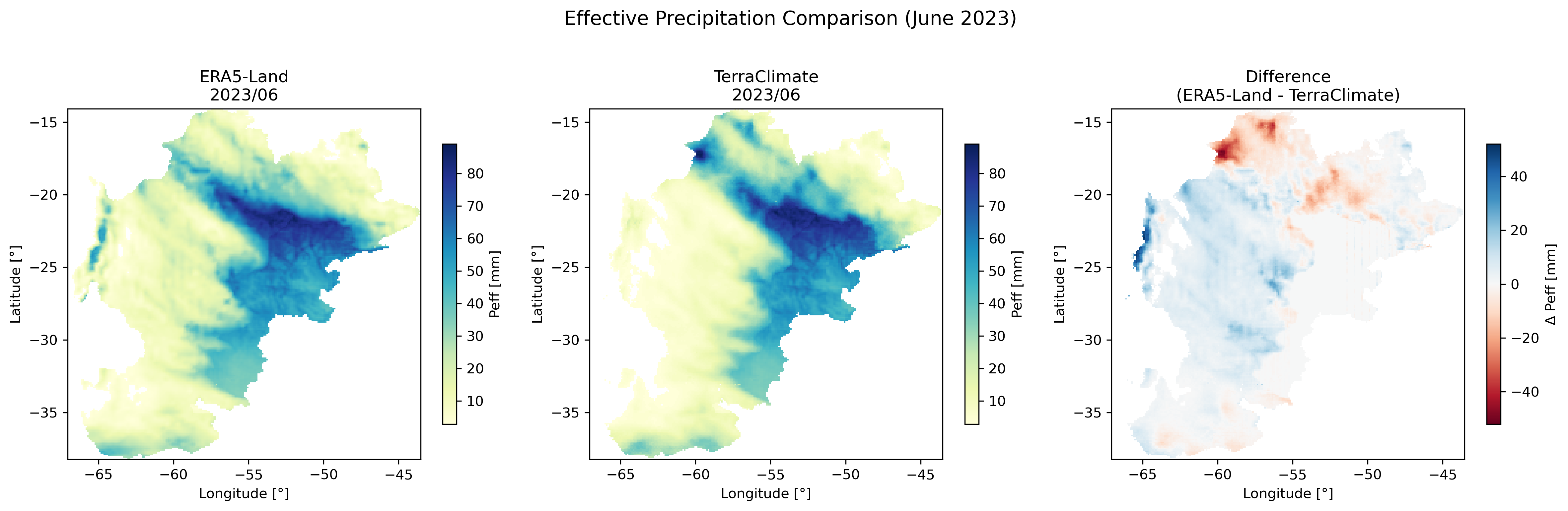
Side-by-side comparison of ERA5-Land and TerraClimate effective precipitation with difference map.
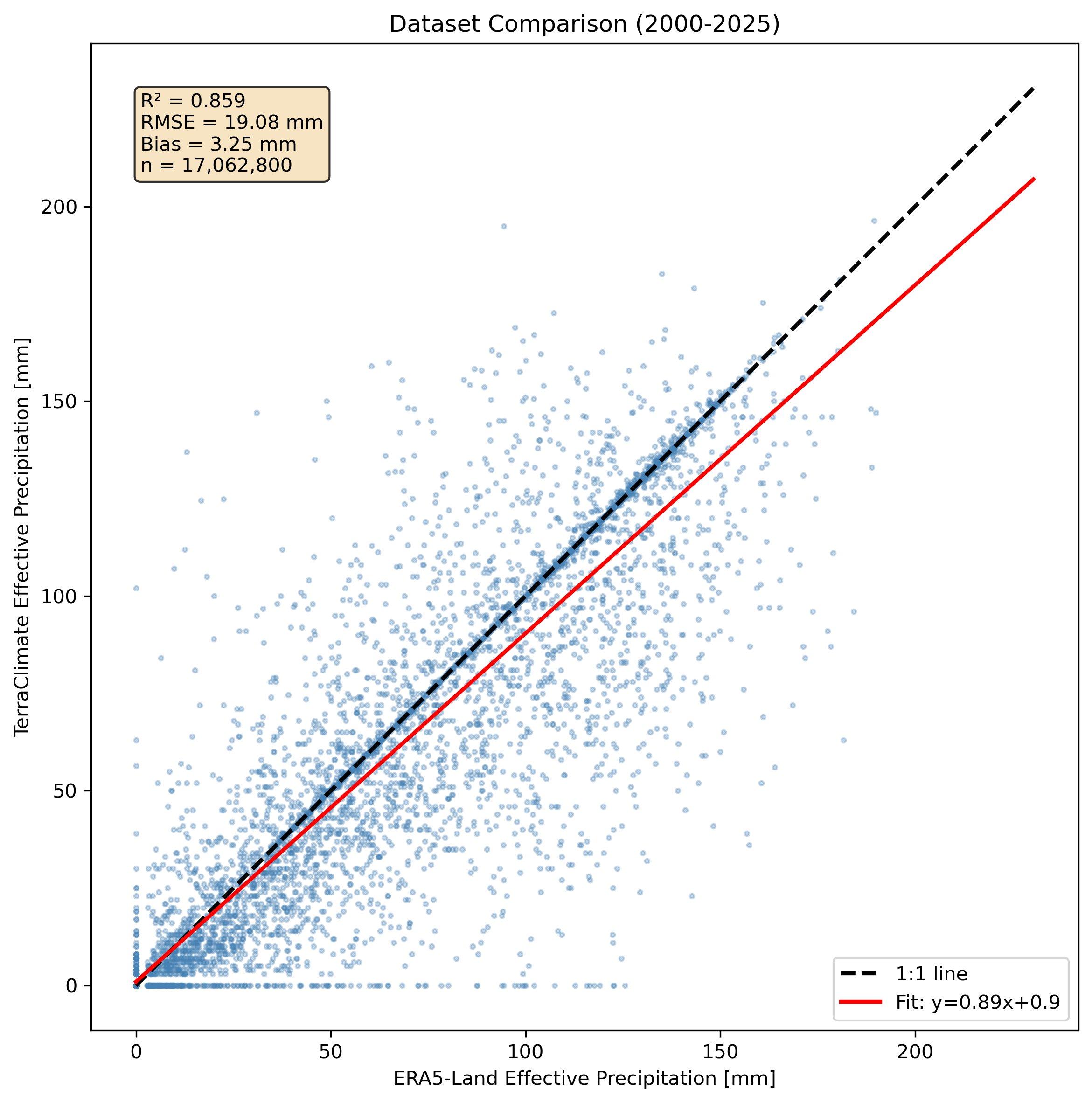
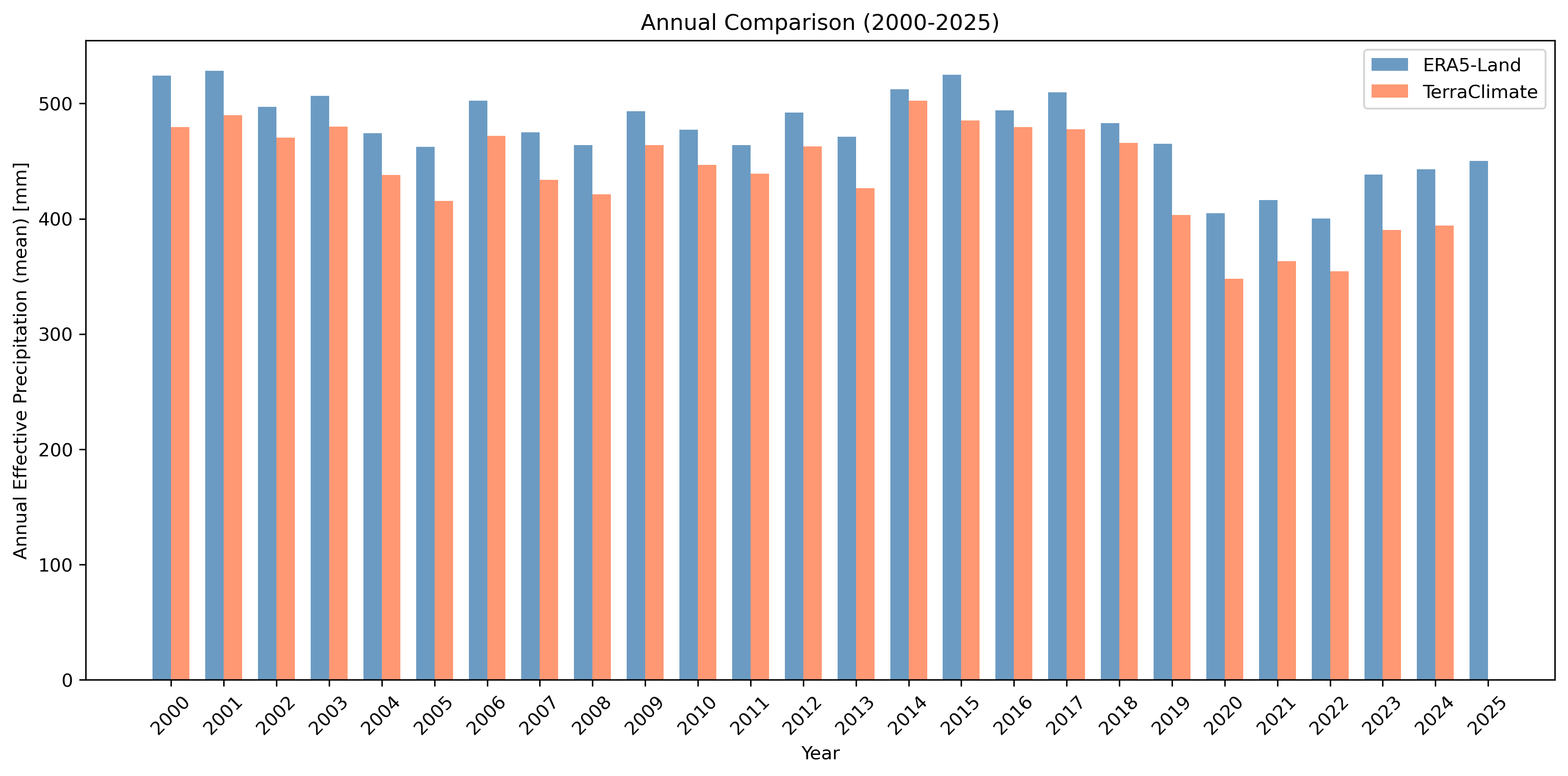
Left: Scatter plot comparison with R², RMSE, and bias statistics. Right: Annual totals comparison.
Zonal statistics comparison between ERA5-Land and TerraClimate for Eastern and Western Rio de la Plata regions.
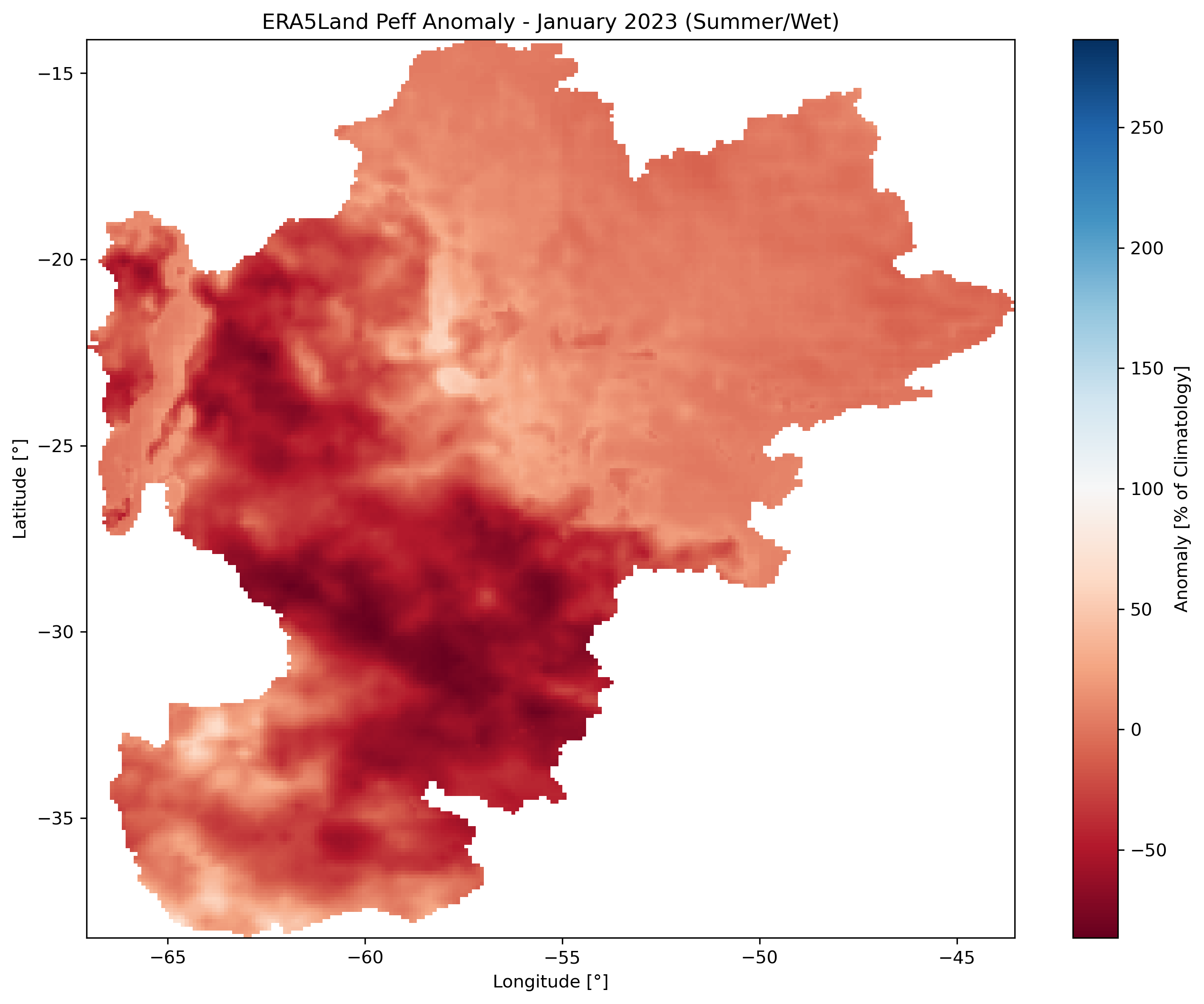
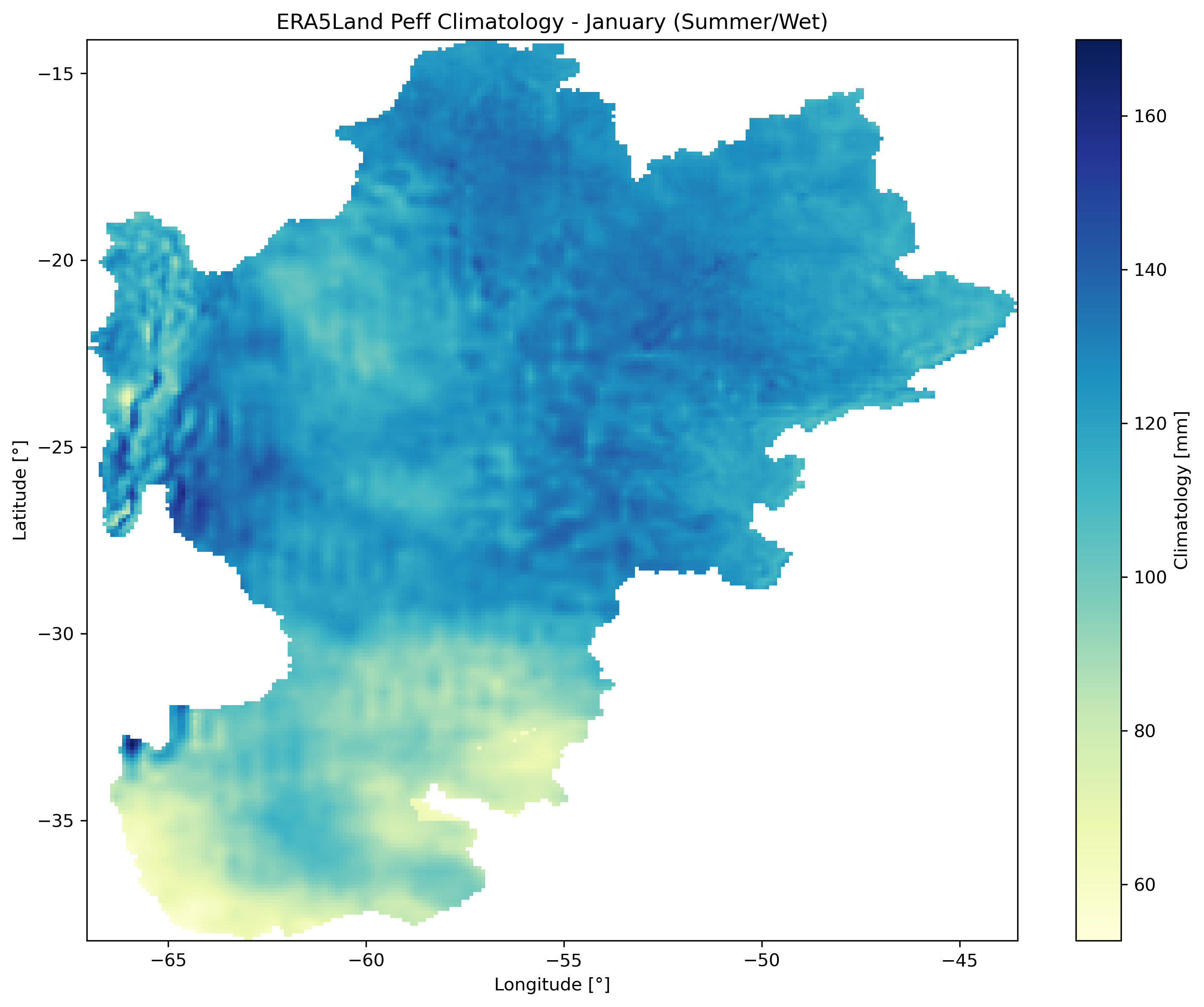
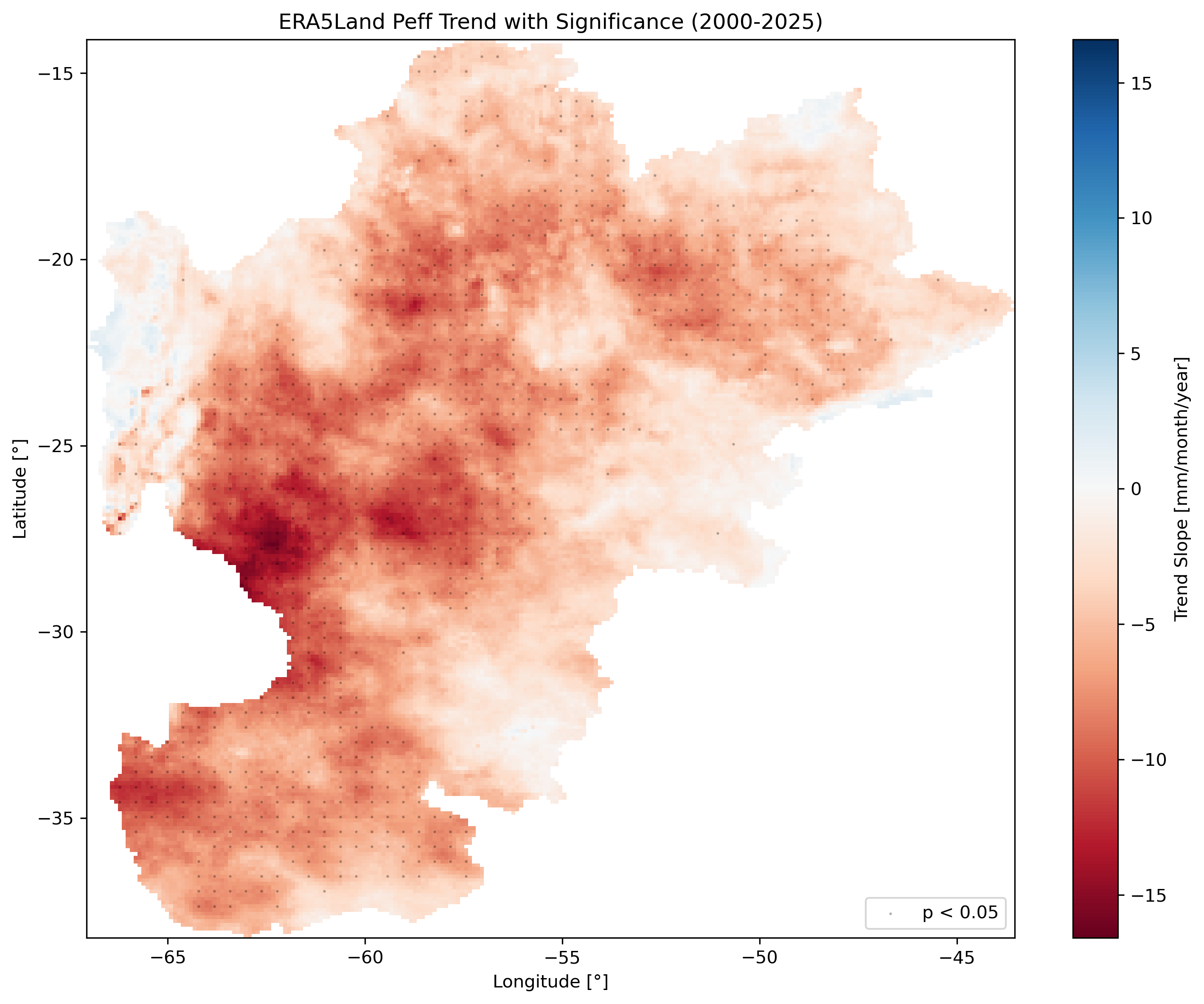
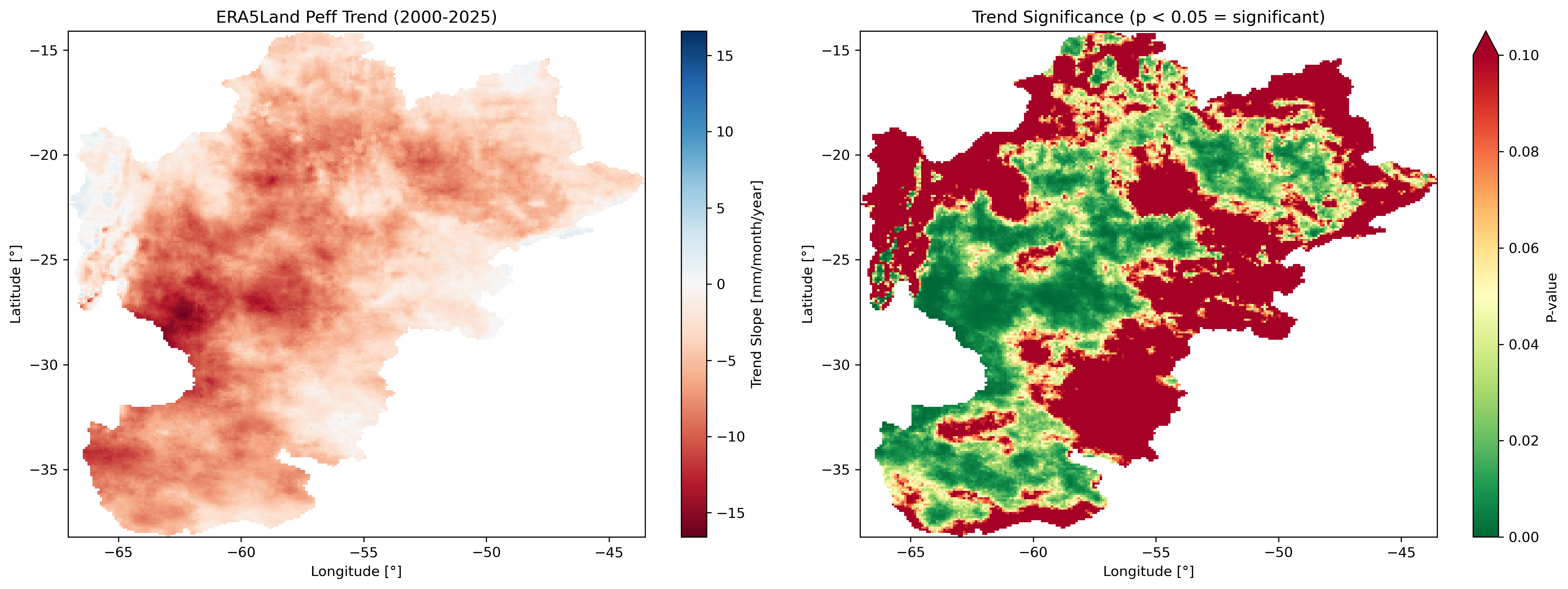
Left: Percent anomaly (January 2023). Center: January climatology (2000-2020). Right: Long-term trend with significance stippling (p < 0.05).
Trend analysis panel showing slope (mm/year) and p-value maps side by side.
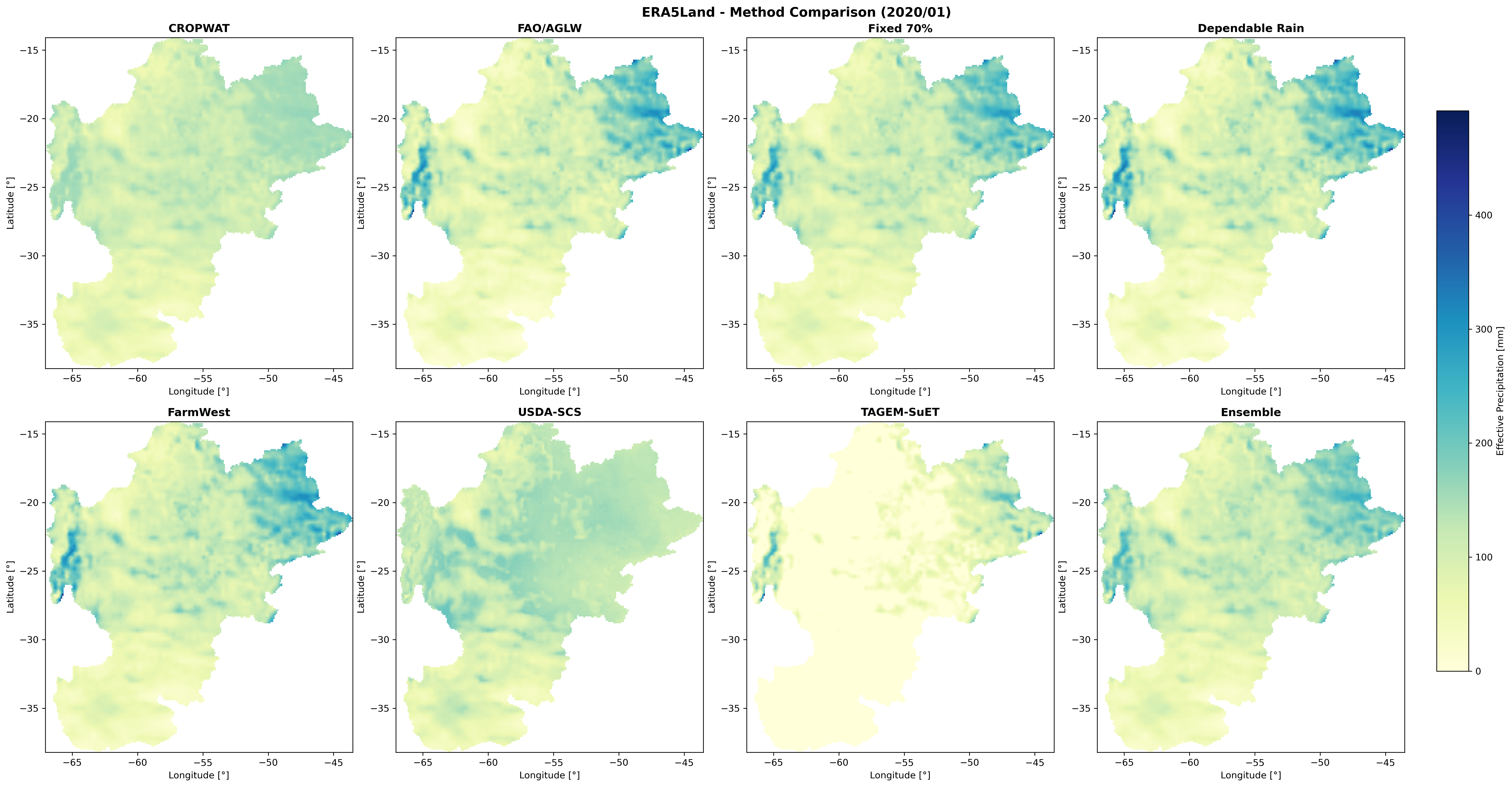
Comparison of 8 effective precipitation methods: CROPWAT, FAO/AGLW, Fixed Percentage (70%), Dependable Rainfall (80%), FarmWest, USDA-SCS, TAGEM-SuET, and Ensemble.
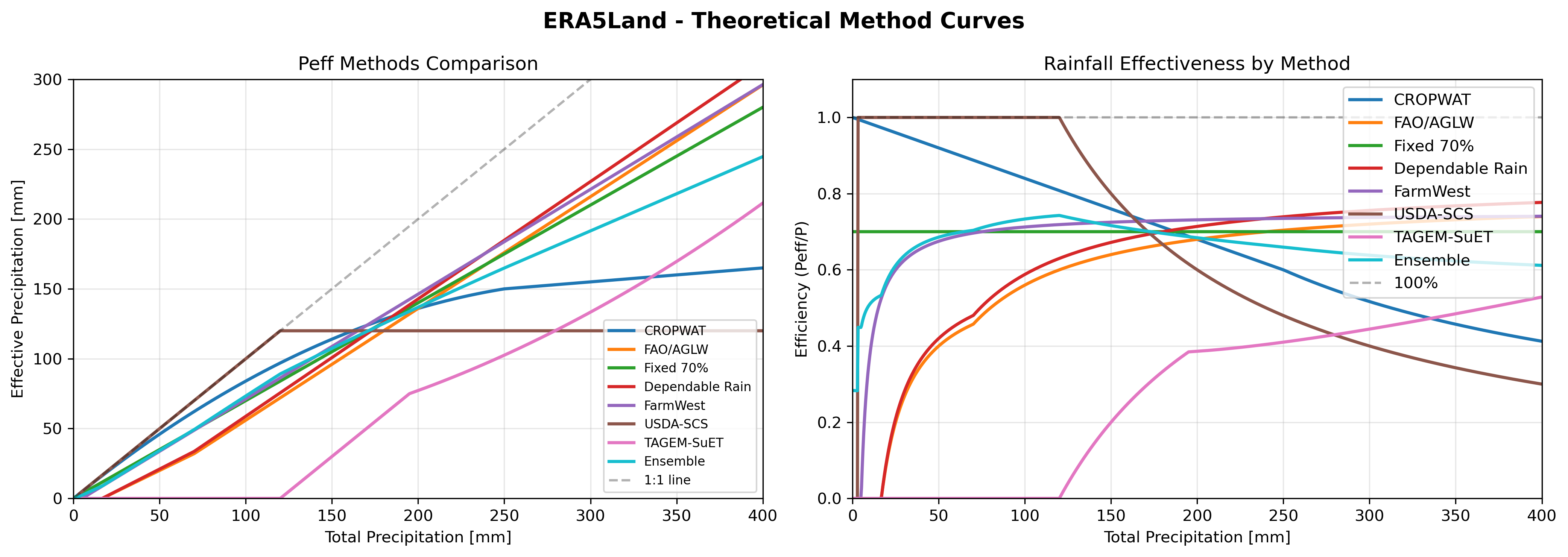
Theoretical response curves for different effective precipitation methods.
The Arizona workflow (Examples/arizona_example.py) demonstrates U.S.-specific datasets with the USDA-SCS method:
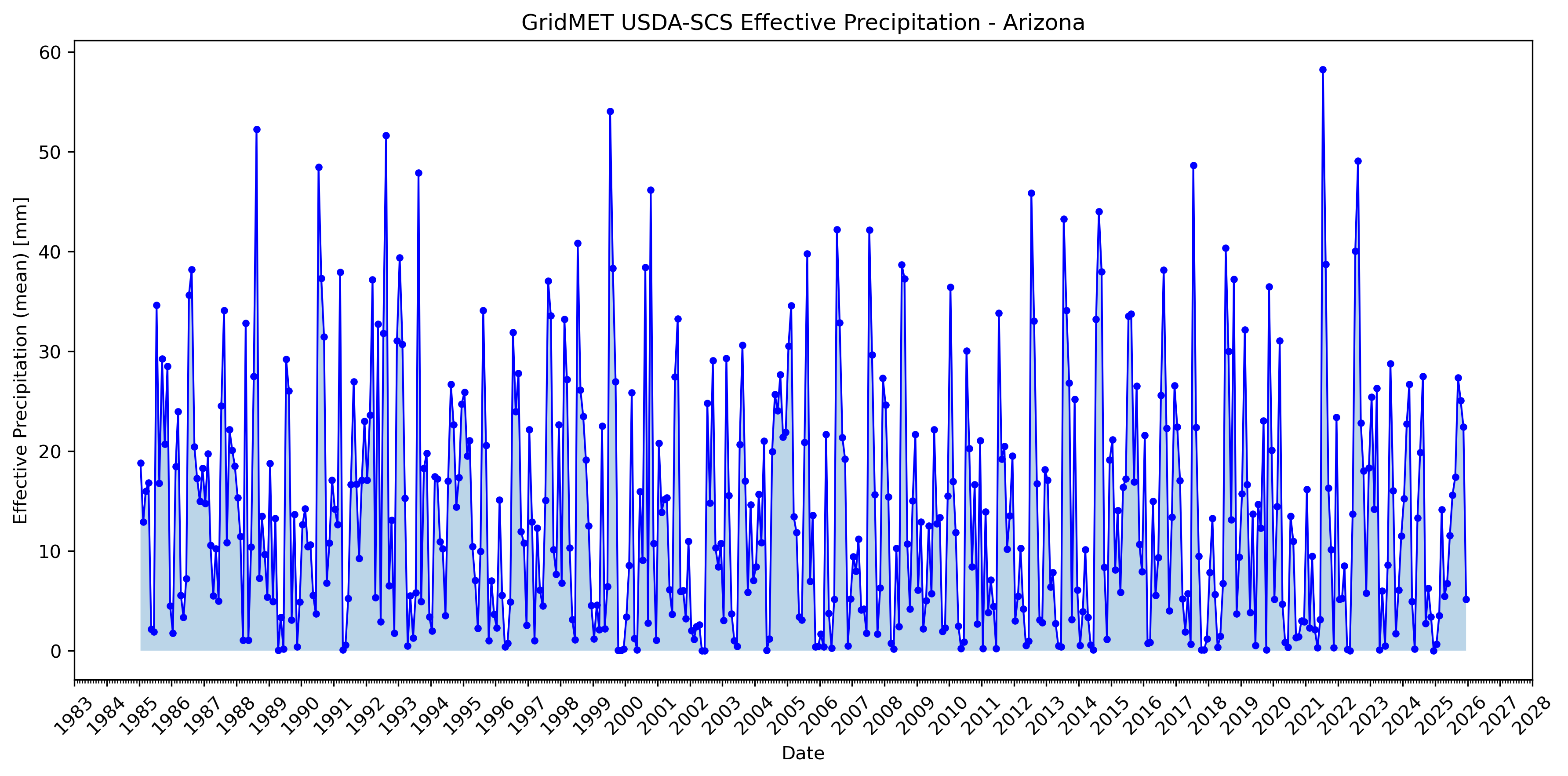
GridMET USDA-SCS effective precipitation for Arizona: time series (left) and monthly climatology (right).
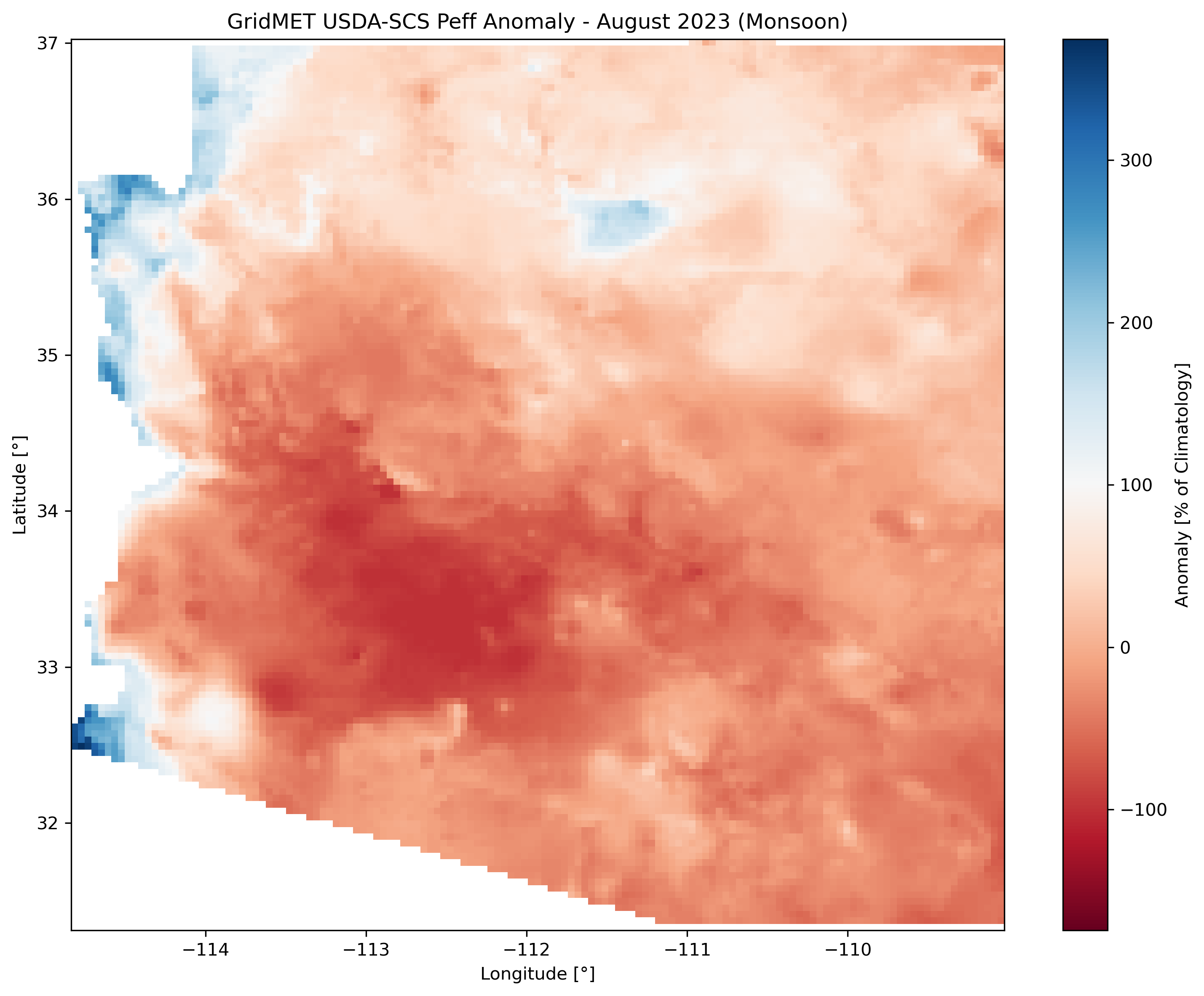
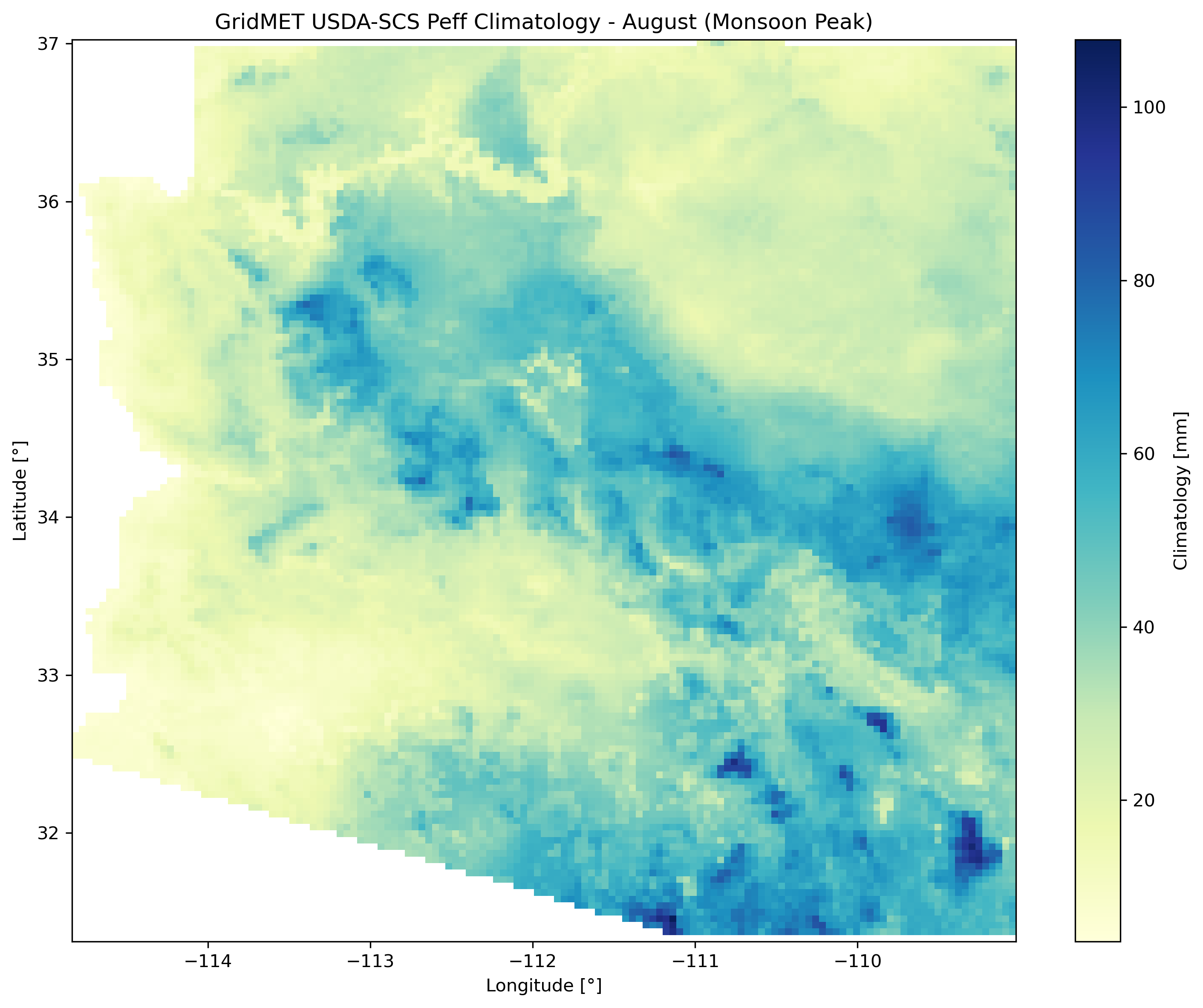
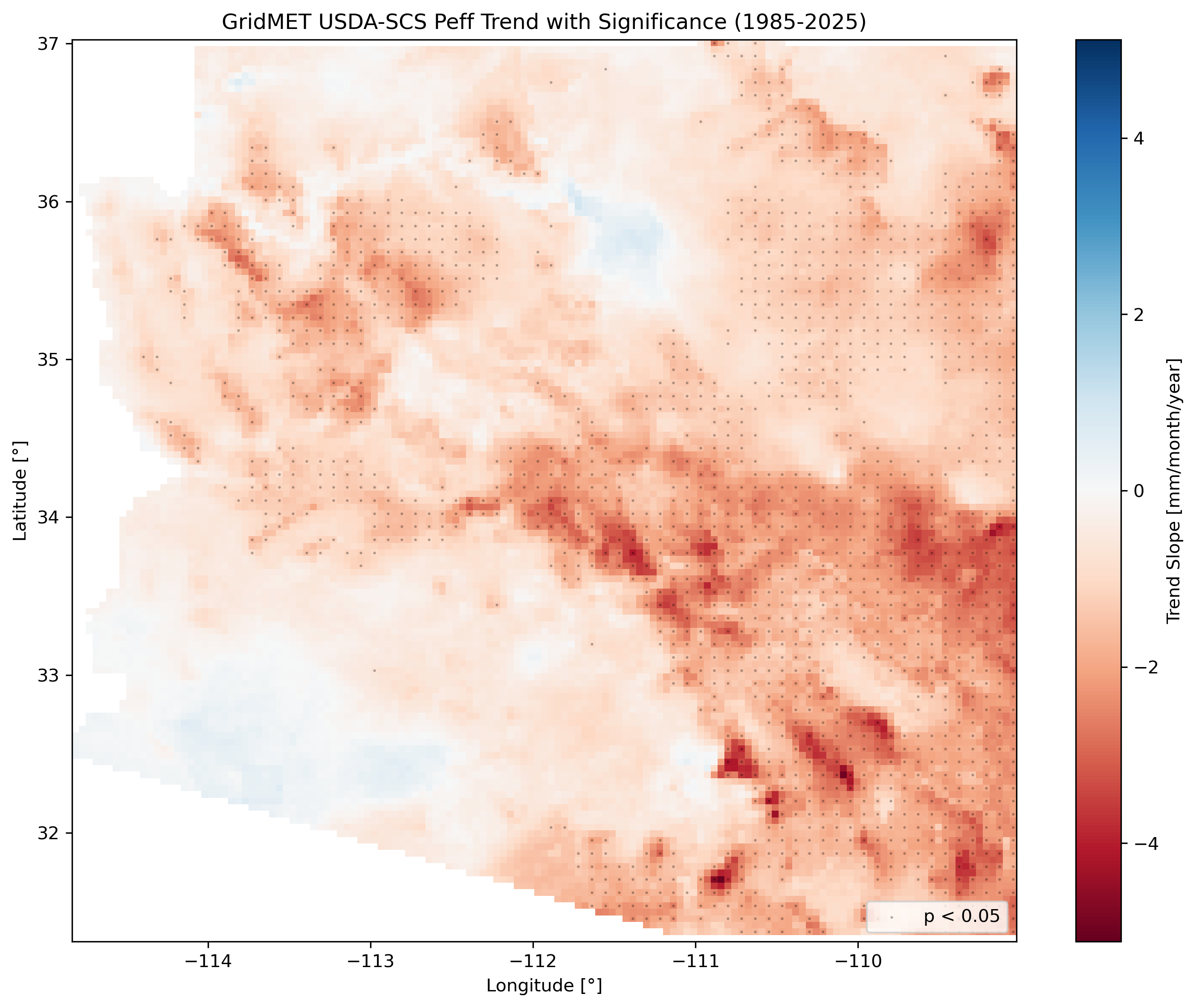
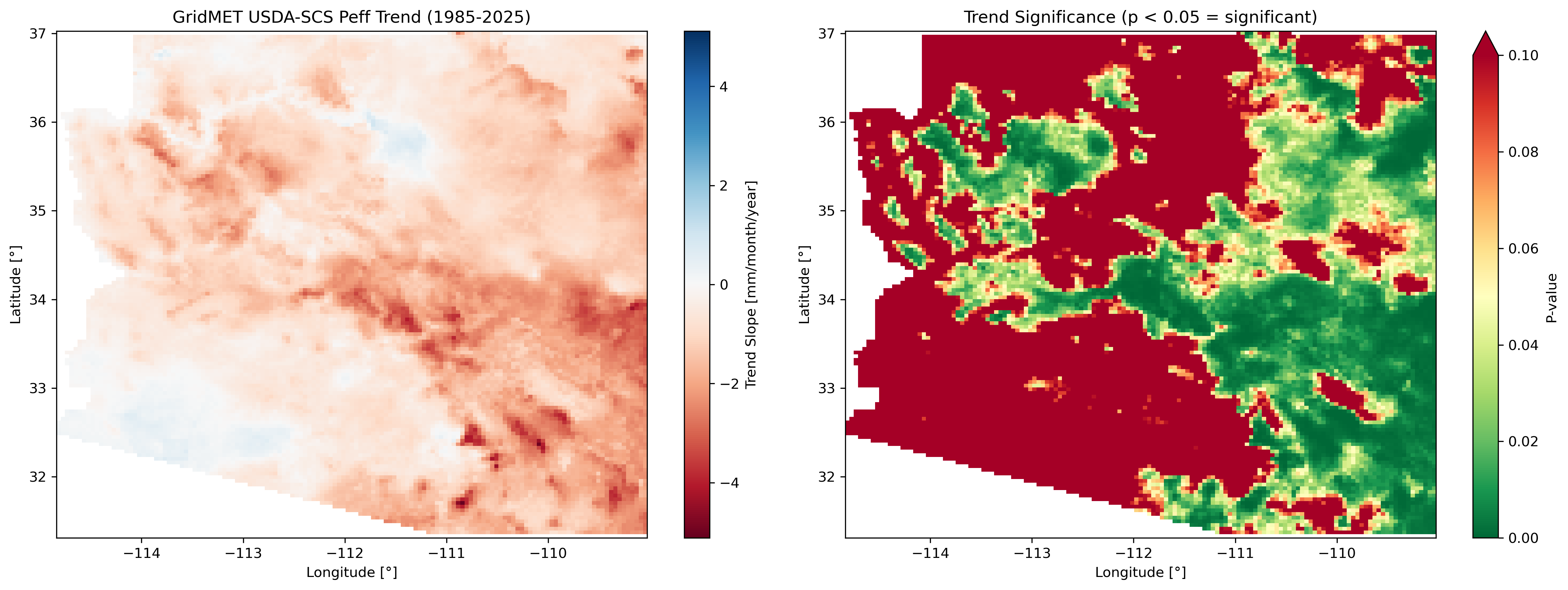
Left: August 2023 anomaly (monsoon season). Center: August climatology (monsoon peak). Right: Long-term trend with significance stippling.
Trend analysis panel for Arizona showing slope and p-value maps.
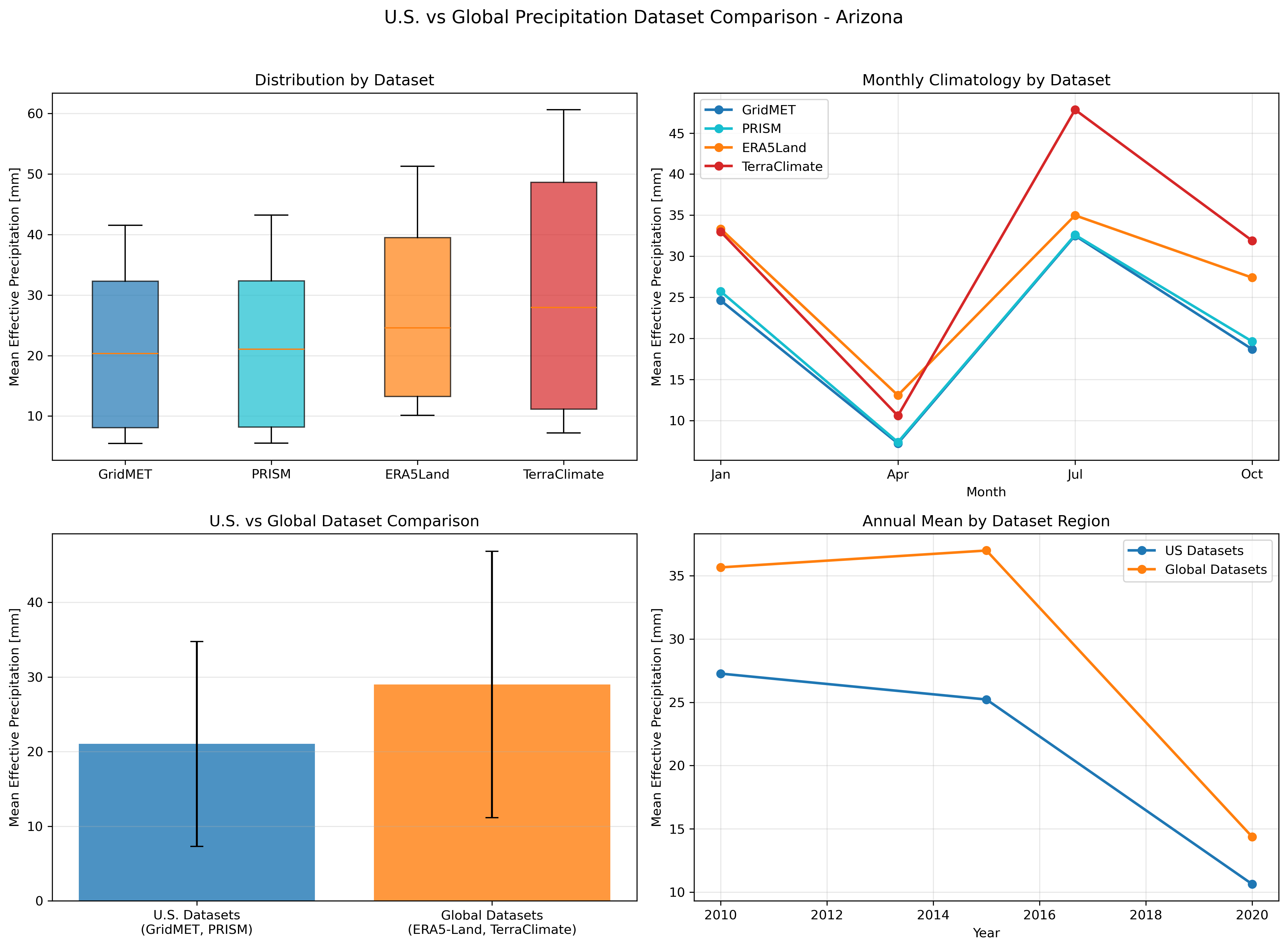
Comparison of U.S. datasets (GridMET, PRISM) vs Global datasets (ERA5-Land, TerraClimate) for Arizona.
The New Mexico workflow (Examples/new_mexico_example.py) compares 8 effective precipitation methods using PRISM data (excludes PCML):
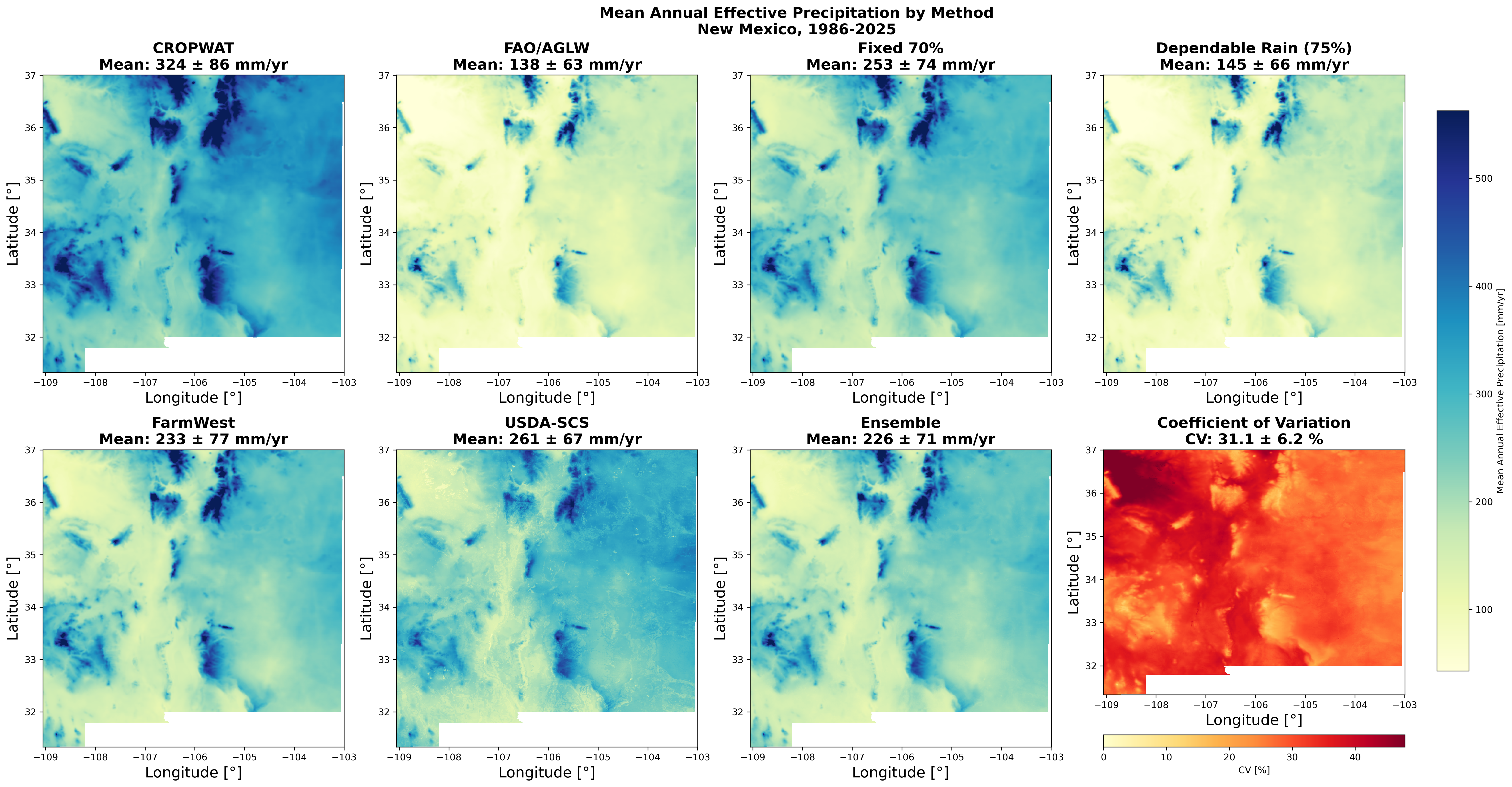
Mean annual effective precipitation (1986-2025) for 8 methods: CROPWAT, FAO/AGLW, Fixed 70%, Dependable Rainfall, FarmWest, USDA-SCS, TAGEM-SuET, and Ensemble.
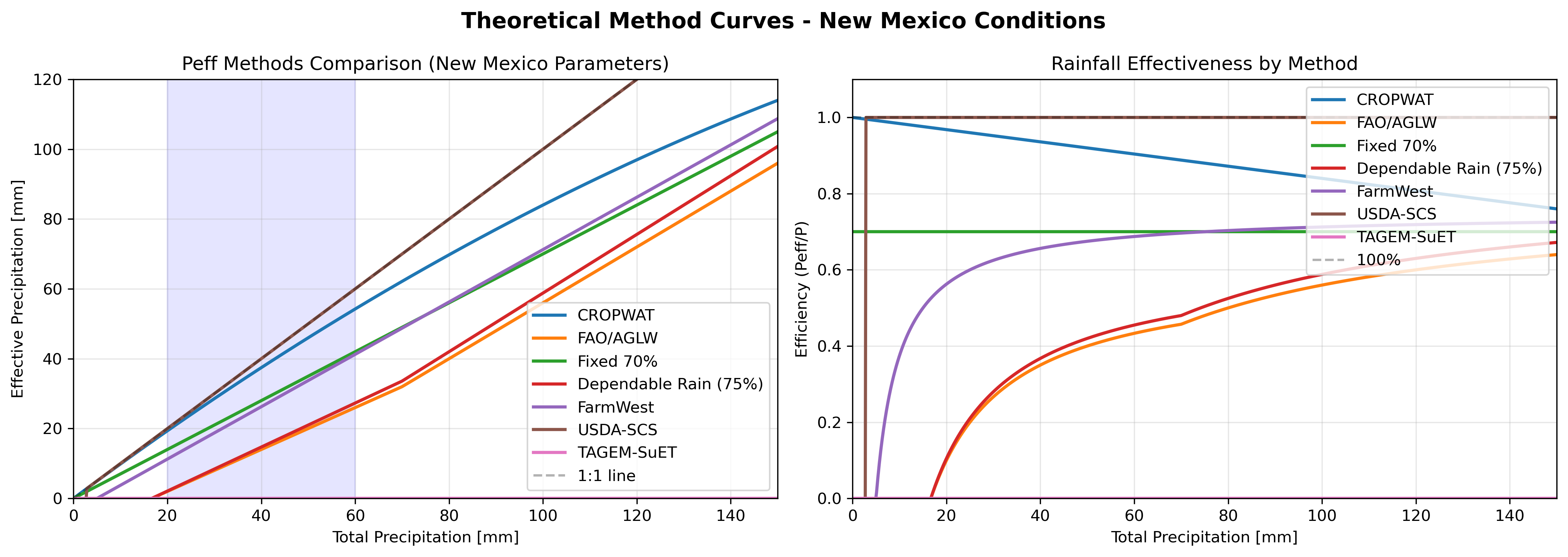
Theoretical response curves for 8 effective precipitation methods using New Mexico typical values (AWC=120mm/m, ETo=200mm/month).
The Western U.S. PCML workflow (Examples/western_us_pcml_example.py) demonstrates the Physics-Constrained Machine Learning method for the entire Western United States:
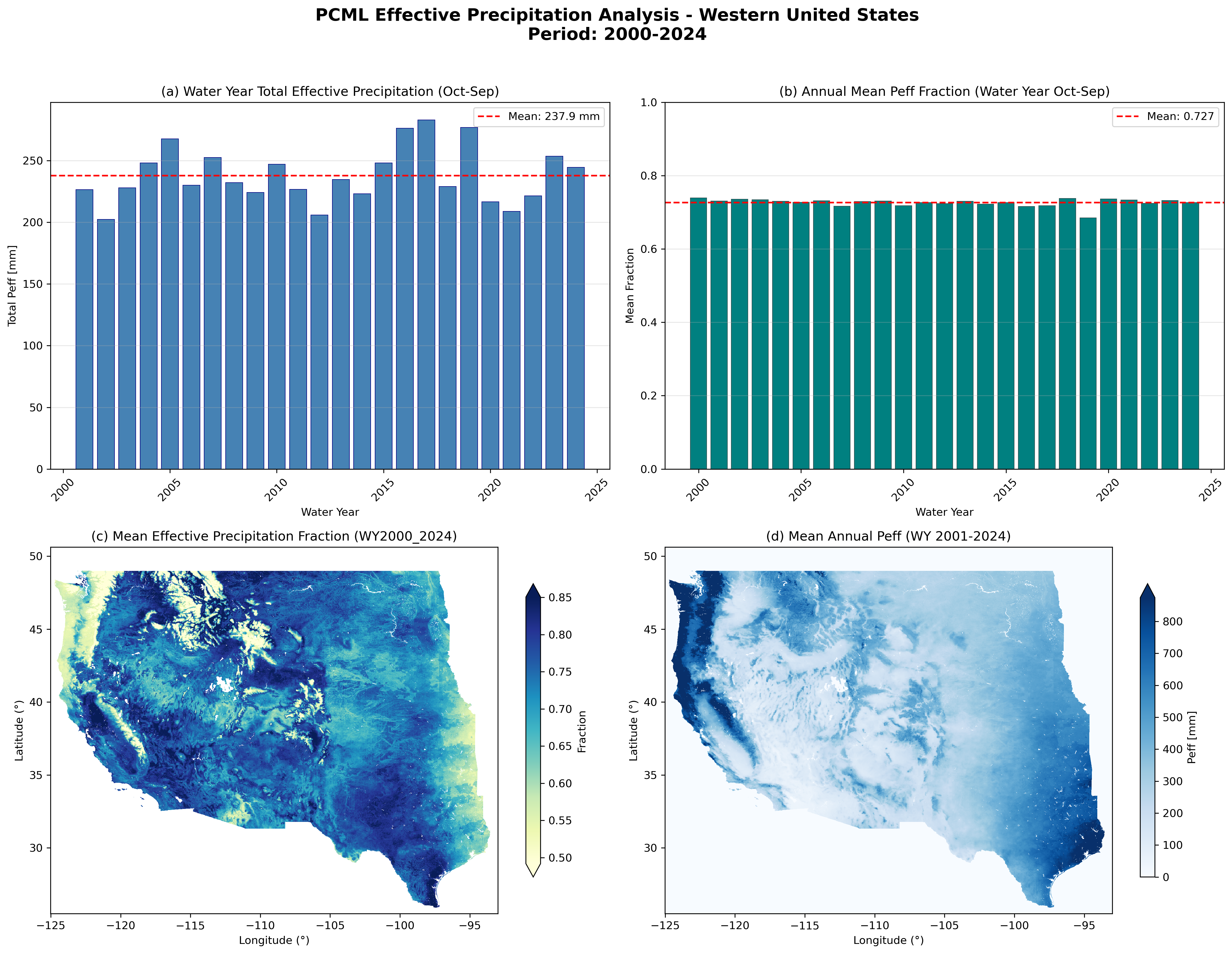
Summary of PCML effective precipitation analysis for the Western U.S. (WY 2001-2024): (a) Water year total time series, (b) Annual mean fraction time series, (c) Mean effective precipitation fraction map, (d) Mean annual effective precipitation map.
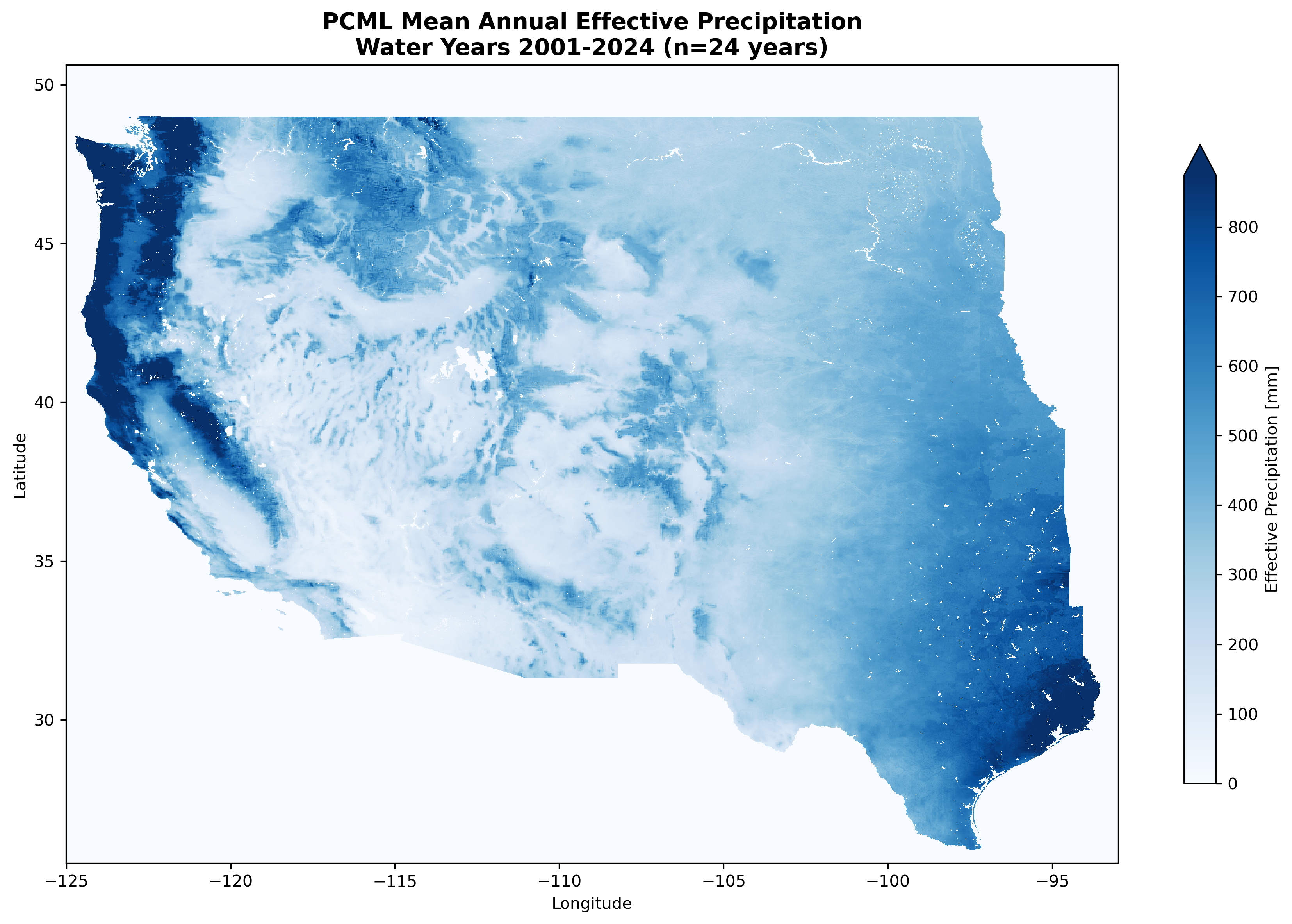
Mean annual effective precipitation (WY 2001-2024) for the Western United States computed from the PCML GEE asset.
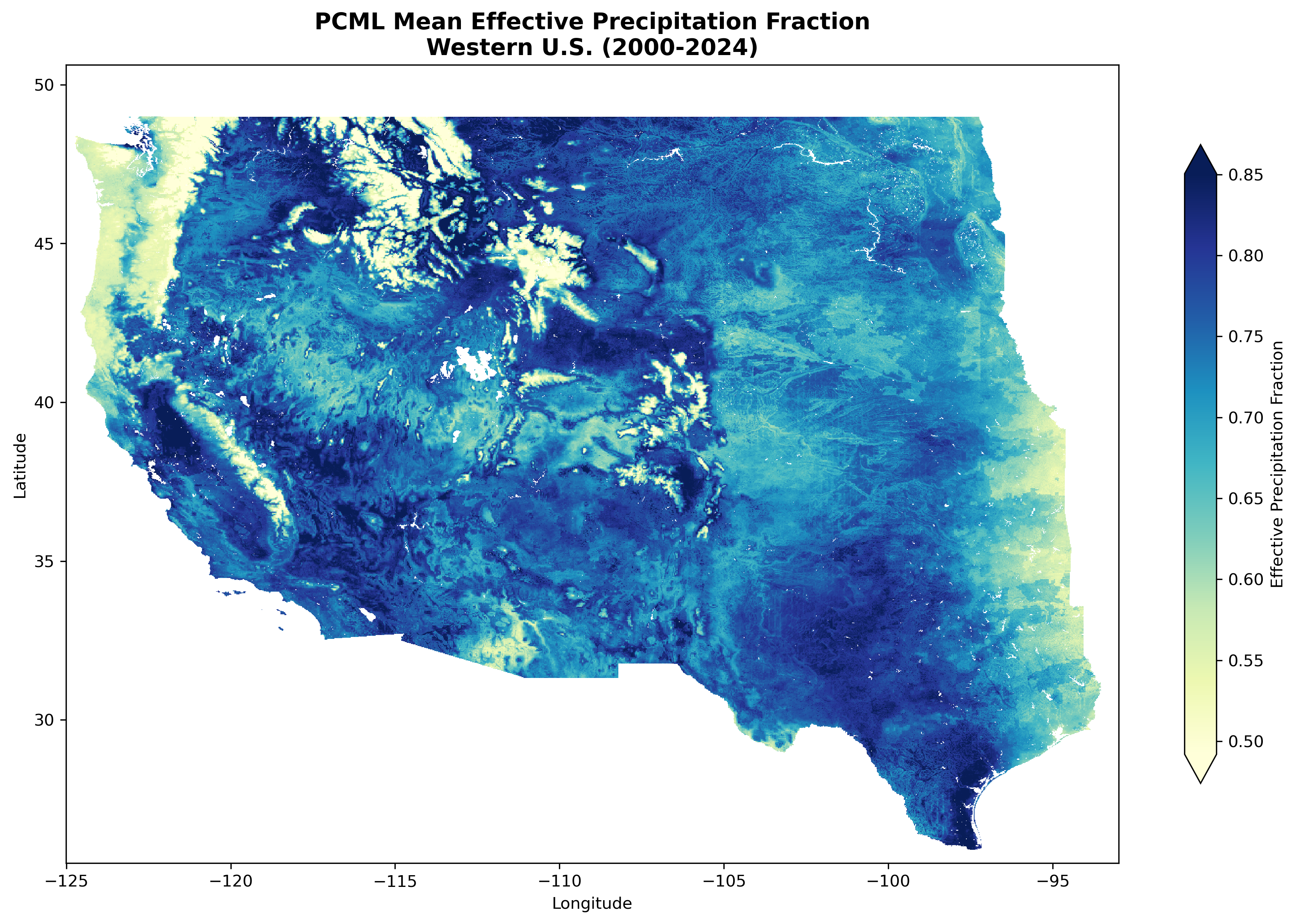
Mean annual effective precipitation fraction (Peff/Precip) for the Western United States (WY 2001-2024).
The Upper Colorado River Basin workflow (Examples/ucrb_example.py) demonstrates field-scale effective precipitation using existing precipitation volumes in a GeoPackage:
- No GEE precipitation download - Works with pre-existing monthly precipitation volumes
- Field-level analysis - Individual agricultural parcels with unique identifiers
- Zonal AWC statistics - Downloads SSURGO AWC data and calculates mean per field
- Unit conversion - Handles acre-feet ↔ mm for method application
- 8 methods - CROPWAT, FAO/AGLW, Fixed 70%, Dependable Rain, FarmWest, and 3 USDA-SCS variants
Precipitation volume (acre-feet)
→ ÷ field area (acres) → depth (feet)
→ × 304.8 → depth (mm)
→ Apply pyCropWat method
→ ÷ 304.8 → depth (feet)
→ × field area (acres)
Effective precipitation volume (acre-feet)
import numpy as np
from pycropwat.methods import cropwat_effective_precip
# Convert acre-feet volume to mm depth
FT_TO_MM = 304.8
ppt_mm = (ppt_volume_acft / area_acres) * FT_TO_MM
# Apply pyCropWat method
peff_mm = cropwat_effective_precip(ppt_mm)
# Convert back to volume
peff_acft = (peff_mm / FT_TO_MM) * area_acresFor more examples and detailed API usage, see the Examples documentation.
Before using pyCropWat, authenticate with Google Earth Engine:
earthengine authenticateOr in Python:
import ee
ee.Authenticate()
ee.Initialize(project='your-project-id')If you use pyCropWat in your research, please cite:
@software{pycropwat,
author = {Majumdar, Sayantan and ReVelle, Peter and Pearson, Christopher and Nozari, Soheil and Minor, Blake A. and Hasan, M. F. and Huntington, Justin L. and Smith, Ryan G.},
title = {pyCropWat: A Python Package for Computing Effective Precipitation Using Google Earth Engine Climate Data},
year = {2026},
url = {https://github.com/montimaj/pyCropWat},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.18201619}
}-
Muratoglu, A., Bilgen, G. K., Angin, I., & Kodal, S. (2023). Performance analyses of effective rainfall estimation methods for accurate quantification of agricultural water footprint. Water Research, 238, 120011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.120011
-
Smith, M. (1992). CROPWAT: A computer program for irrigation planning and management (FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 46). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. https://www.fao.org/sustainable-development-goals-helpdesk/champion/article-detail/cropwat/en
This work was supported by a U.S. Army Corps of Engineers grant (W912HZ25C0016) for the project "Improved Characterization of Groundwater Resources in Transboundary Watersheds using Satellite Data and Integrated Models."
Principal Investigator: Dr. Ryan Smith (Colorado State University)
Co-Principal Investigators:
- Dr. Ryan Bailey (Colorado State University)
- Dr. Justin Huntington (Desert Research Institute)
- Dr. Sayantan Majumdar (Desert Research Institute)
- Mr. Peter ReVelle (Desert Research Institute)
Research Scientist:
- Dr. Soheil Nozari (Colorado State University)
The following features have been implemented or are under consideration for future releases:
- ✅ Seasonal summaries (DJF, MAM, JJA, SON)
- ✅ Annual totals with statistics
- ✅ Growing season aggregations based on crop calendars
- ✅ Custom date range aggregations
- ✅ Long-term climatology (e.g., 30-year normals)
- ✅ Anomaly detection (absolute, percent, standardized)
- ✅ Trend analysis using linear regression or Theil-Sen/Mann-Kendall
- ✅ Zonal statistics for polygons
- ✅ FAO/AGLW method
- ✅ Fixed percentage method (configurable percentage)
- ✅ Dependable rainfall (FAO method at different probability levels)
- ✅ FarmWest method (Pacific Northwest irrigation)
- ✅ USDA-SCS method (soil moisture depletion with AWC and ETo)
- ✅ TAGEM-SuET method (P - ETo with 75mm cap)
- ✅ PCML method (Physics-Constrained ML for Western U.S., Jan 2000 - Sep 2024)
- ✅ Ensemble method (mean of 6 methods, excludes TAGEM-SuET and PCML)
- ✅ South America example (Rio de la Plata, 8 methods)
- ✅ Arizona example (U.S. vs Global datasets, 8 methods)
- ✅ New Mexico example (PRISM with IrrMapper mask, 8 methods)
- ✅ Western U.S. PCML example (17 states, water year aggregation)
- ✅ UCRB field-scale example (GeoPackage with AWC lookup)
- ✅ NetCDF output for time-series analysis
- ✅ Cloud-Optimized GeoTIFFs (COGs)
- ✅ Zonal statistics CSV export by polygon
- ✅ Built-in plotting functions for time series
- ✅ Monthly climatology bar charts
- ✅ Raster map visualization
- ✅ Interactive maps (folium/leafmap integration)
- ✅ Comparison plots between datasets (side-by-side, scatter, annual)
- Crop coefficient (Kc) integration for different crop types/stages
- Net irrigation requirement (ETc - Peff) calculations
- Crop calendar support for region-specific growing seasons
- Drought indices (SPI, SPEI) integration
- Direct cloud storage export (GCS, S3)
- Station data comparison module
- Cross-dataset validation (e.g., ERA5 vs TerraClimate)
- Uncertainty quantification
- Evapotranspiration integration (from MODIS, SSEBop, OpenET)
- Simple water balance (P - ET - Runoff)
Have a feature request? Please submit your ideas via GitHub Issues. We welcome community contributions and feedback!
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.