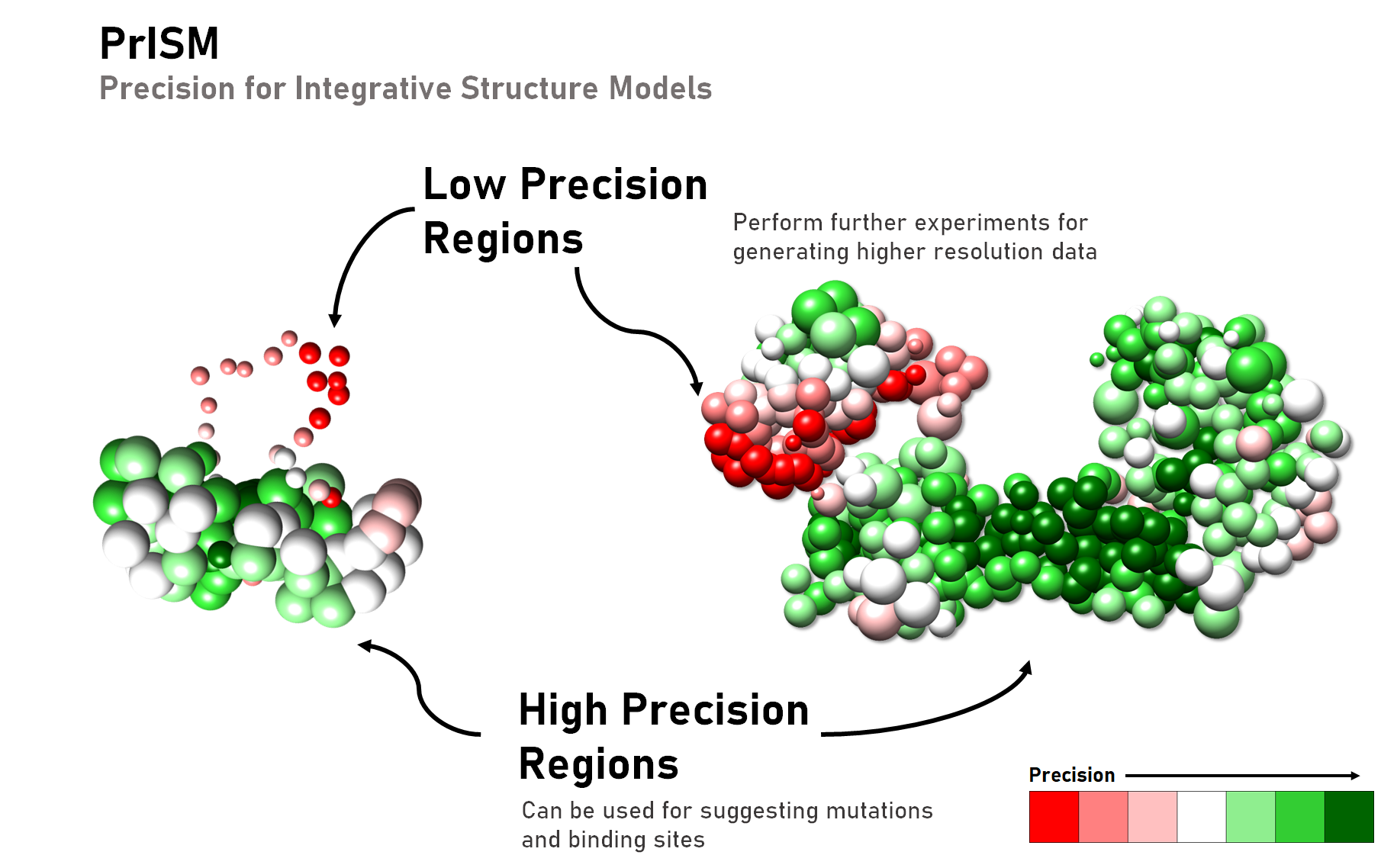
\brief PrISM is a package for visualizing regions of high and low precision in ensembles of integrative models.
PrISM is a package for visualizing regions of high and low precision in ensembles of integrative models. It annotates structural patches with similar levels of precision in a scalable and efficient manner for ensembles of large macromolecular assemblies.
-
Varun Ullanat, Nikhil Kasukurthi, Shruthi Viswanath, PrISM: precision for integrative structural models, Bioinformatics, 38(15), 3837–3839, 2022 at DOI.
-
Data is deposited in Zenodo.
PrISM requires IMP to be installed.
Ensure that the analysis module sampcon is also installed (if installing IMP from source: clone sampcon from github into its module directory and recompile IMP).
It also requires a list of python packages that can be installed with the following types of commands:
pip3 install --user -r requirements.txt
or
pip install -r requirements.txt
The primary input for PrISM is a set of structurally superposed integrative models for a macromolecular assembly. This can be in any of the following formats below. See examples for usage of each type.
PrISM requires bead coordinates, masses, radii, and bead names of the models as single numpy array file. This can be directly obtained for each cluster of models from the integrative modeling analysis pipeline by using the --prism flag in sampcon. This is the recommended way to obtain inputs for PrISM.
Run PrISM with downloaded mmCIF PDBDEV file in ihm mode.
Run PrISM with either a single RMF3 file contaiing multiple models or a folder of RMF3 files each contaiing 1 or more models. For efficiency provide a single RMF3 file by concatenating all models from all RMF3 files into one.
PrISM supports Protein Data Bank (.pdb) files of structurally superposed model ensembles.
PrISM supports Protein Data Bank (.cif) files of structurally superposed model ensembles.
PrISM can read binary DCD (.dcd) files for atomic coordinates of integrative models. Here a representative RMF file would also be required to read the mass, radius and particle name of each bead.
There are two outputs at the end of a successful run. The first, annotations_cl*.txt, provides bead-wise records of the bead name, type (high, low or medium precision), class, patch identity and bead spread value. This is used as the input to the color_precision.py script. The second type of files, low_prec.txt and high_prec.txt gives bead composition for low and high precision patches respectively.
Use src/main.pyto generate the precision for the given input. Use the --help option to generate descriptions of arguments.
Here, we assume you are in the example/Actin directory which contains the cluster.0.prism.npz file as input to PrISM and a cluster representative model actin_cluster_center_model.rmf3 to visualize the results.
The following command runs PrISM for given set of inputs and arguments:
python ../../src/main.py --input cluster.0.prism.npz --input_type npz --output output/ --voxel_size 4 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50
Here, the annotated patches are obtained for 2 classes each for both low and high precision.
In the `example/Gtusc' directory, run the following to obtained annotated patches for 3 classes:
python ../../src/main.py --input cluster.0.prism.npz --input_type npz --output output/ --voxel_size 4 --return_spread --classes 3 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50
The voxel size of the grid used to calulate densities can be changed by varying the voxel_size parameter. In the example/Tfiih directory, run the following:
python ../../src/main.py --input cluster.0.prism.npz --input_type npz --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50
For an IMP entry (PDBDEV_00000025):
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/main.py --input ./PDBDEV_00000025.cif --input_type ihm --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50 --resolution 1
For a non-IMP entry (PDBDEV_00000044):
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/main.py --input ./PDBDEV_00000044.cif --input_type ihm --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50 --resolution 1
NOTE: No need to run the step 2. below separately in case of IHM input. Coloring is generated on the fly.
For RMF files, the input would be the directory containing the RMF files.
Set the parameters resolution (coarse-grained bead-resolution in a multi-scale system; precision is annotated only one beads of a single resolution), subunit (if only a single subunit needs to be annotated) and selection (if subsets of the system comprising of multiple subunits/domains need to be annotated). These options are similar to what was used in the integrative modeling analysis pipeline.
The selection defaults to resolution=30 (30 residues per bead); all subunits are selected by default.
In the example/rmfs directory, run the following:
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/main.py --input . --input_type rmf --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50 --resolution 30
Here $IMP is the path to local installation of IMP (if compiled from source). If IMP has been installed using a binary installer, the $IMP/build/setup_environment.sh argument may be skipped.
For PDB files, ensure that the return_spread flag is present. The input here would be the directory containing the PDB files. In the example/pdbs directory, run the following:
python ../../src/main.py --input . --input_type pdb --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50
For MMCIF files, ensure that the return_spread flag is present. The input here would be the directory containing the MMCIF files. In the example/mmcif directory, run the following:
python ../../src/main.py --input . --input_type cif --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50
First download the cluster.0.dcd file from the given link into the example/dcd folder. In the same folder, run the following:
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/main.py --input . --input_type dcd --output output/ --voxel_size 2 --return_spread --classes 2 --cores 16 --models 1.0 --n_breaks 50 --resolution 1
NOTE: DCD files from IMP usually have models deposited at resolution = 1. So run PrISM with resolution =1 for these types of models.
- Increase the
voxel_sizeparameter if you are out of memory or if computation takes a lot of time. - Increase the
n_breaksparameter if memory consumption is high. However, this will increase the time taken. - Decrease the fraction of models (
models) parameter if iterating through the input models is taking a long time. This selects a random fraction of models for precision calculation. - Use selection mode (
-sn) in sampcon if some parts of the system were fixed during sampling. This avoids having to calculate patches on the fixed parts. - For multi-scale systems use the coarsest resolution (
-r) in sampcon to speed up precision calculation in PrISM.
The previous main.py command, on running successfully, produces a file annotations.txt in the output directory.
The next command uses information from this file to color the beads of a representative model (e.g., the cluster center model).
For the NPZ and RMF input, the resolution, selection, subunit options i.e. -r, -sn, and -su options should be identical to what was passed in the previous step (main.py) and in the sampcon step exhaust.py.
The representative model is specified by the -i option.
The -o option specifies the name of the output patch-colored RMF file.
For e.g. in example/Actin
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/color_precision.py --resolution 30 --annotations_file output/annotations_cl2.txt --input actin_cluster_center_model.rmf3 --output output/actin_patch_colored_cluster_center_model.rmf3
Here $IMP is the path to local installation of IMP (if compiled from source). If IMP has been installed using a binary installer, the $IMP/build/setup_environment.sh argument may be skipped.
Similary for the Gtusc complex, run the following from example/Gtusc
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/color_precision.py --resolution 10 --annotations_file output/annotations_cl3.txt --input gtusc_cluster_center_model.rmf3 --output output/gtusc_patch_colored_cluster_center_model.rmf3 -su Spc110
Finally, for TFIIH, run the following from example/Tfiih
$IMP/build/setup_environment.sh python ../../src/color_precision.py --resolution 30 --annotations_file output/annotations_cl2.txt --input tfiih_cluster_center_model.rmf3 --output output/tfiih_patch_colored_cluster_center_model.rmf3
Use the color_precision_pdb.py script to color pdb structures using the bead_spread file generated by PrISM. For e.g in example/pdbs
python ../../src/color_precision_pdb.py -i PED00001e001.pdb -t pdb -pf output/bead_spreads_cl2.txt -o output/patch_colored_model.pdb
Use the color_precision_pdb.py script to color pdb structures using the bead_spread file generated by PrISM. For e.g in example/mmcif
python ../../src/color_precision_pdb.py -i PED00001e001.cif -t cif -pf output/bead_spreads_cl2.txt -o output/patch_colored_model.cif
The output RMF file, patch_colored_cluster_center_model.rmf3 can be visualized in UCSF Chimera.
- It may be helpful to view this file along with the representative model simultaneously.
- One can hide/select a set of beads from this hierarchy using the RMF viewer.
- rmfalias might be helpful for selecting/unselection sets of beads.
If run on PDBs, the output PDB file, patch_colored_model.pdb can be visualized in UCSF Chimera or ChimeraX. The precision is in the B-factor field, and can be displayed by for example, clicking on Molecule Display-> B-factor.
Author(s): Varun Ullanat, Kartik Majila, Shruthi Viswanath
Date: April 7th, 2023
License: CC BY-SA 4.0 This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Last known good IMP version: not tested
Testable: Yes
Parallelizeable: Yes
Publications: Ullanat, V., et. al. PrISM: precision for integrative structural models, Bioinformatics, 38(15), 3837–3839, 2022. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac400.