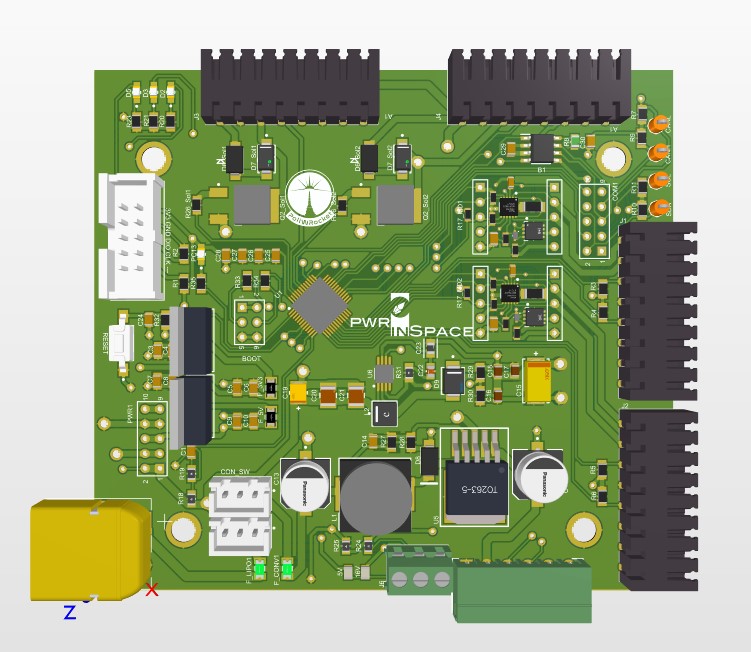
Tanwa - (Tankowanie - Ważenia) Filling and ignition system, STM32 (PWM) + ESP32 (COM)
Filling and ignition system is located on a metal frame close to the launch rail. Its main purpose is to control and supervise process of filling oxidizer from external tank to the tank inside the rocket. Since whole process is controlled remotely, proper sensors and radio communication has to be used. Thanks to remote characteristic of the process it is much more safe for the crew, not exposing anyone to danger.
To control filling, the following components are necessary:
• Valves - hydraulics connected with motors/servos and gearing.
• Limit switches – sensors providing data about valve states.
• Pressure sensor – returning pressure inside hydraulics.
• Quick disconnect – special arm structure with motor, responsible for disconnecting hose from the rocket, when process is finished.
• Scales – weight measurement system, responsible for providing information about amount of oxidizer inside the rocket.
• Radio module – sends frames with crucial data and receives commands to/from ground station.
• Ignition module – redundant ignition system with numerous arming precautions, for firing e-matches.
• SD card – used to store data saved with much higher rate than is sent via radio.
Having all components defined for the system, it was divided into two parts: power with motor control and communication with weight measurement. That is why final system consists of two PCB boards in stack up configuration. The main reason for such division was to lower the risk of introducing noise to the weight measurement. Scales were built based on tensiometers connected in Wheatstone's bridge configuration so that their output is in the form of analog signal. Having high power lines routed near differential pairs of scale's output would certainly affect the readings. Creating two separate printed circuits and connecting them with only necessary and sufficient number of pins, solves this issue.
Communication board is managed by ESP32 in WROOM32D specification microcontroller, which communicates with STM32103C8T6 placed on power board in master-slave configuration via I2C protocol. Major advantage of ESP32 is its ability to operate using WiFi and Bluetooth as well as ESP NOW. ESP NOW protocol allows to build net up to 20 separated devices, which is very convenient for different modules communicating remotely for short distance. In this case, filling and ignition system is able to communicate with the rocket's computer (OBC), sending and receiving information.
For radio communication with ground station, LoRa device is used. It was used due to its capabilities - excellent price to performance ratio and special LoRa patented modulation, being much better than commonly used FSK or OOK. It is worth to mention, that thanks to LoRa's chirp modulation and spread spectrum it is able to receive and retrieve data correctly even if SNR is negative.
As mentioned above, weight measurement is realized using tensiometers and Analog to Digital Converters amplifying and converting analog signal into bit stream. In this project HX711 ADCs were used. Data is sent to the MCU (ESP32) via two line digital interface. MCU computes mass and provides output in given units (namely grams). Due to resistive characteristics of the tensiometers and sensitivity of integrated circuits on temperature it occurred necessary to determine this influence and describe it with mathematical formula compensating errors. This is important, especially on the desert where launch rail can stand in full sun for many hours.
Responsibilities:
COM - Jakub Zatoń
PWR - Filip Kulisiewicz